Lbl2Vec learns jointly embedded label, document and word vectors to retrieve documents with predefined topics from an unlabeled document corpus.
Project description
Lbl2Vec
Lbl2Vec is an algorithm for unsupervised document classification and unsupervised document retrieval. It automatically generates jointly embedded label, document and word vectors and returns documents of topics modeled by manually predefined keywords. This package includes two different model types. The plain Lbl2Vec model uses Doc2Vec, whereas Lbl2TransformerVec uses transformer-based language models to create the embeddings. Once you train a model you can:
- Classify documents as related to one of the predefined topics.
- Get similarity scores for documents to each predefined topic.
- Get most similar predefined topic of documents.
See the papers introducing Lbl2Vec and Lbl2TransformerVec for more details on how it works.
Corresponding Medium post describing the use of Lbl2Vec for unsupervised text classification can be found here.
Benefits
- No need to label the whole document dataset for classification.
- No stop word lists required.
- No need for stemming/lemmatization.
- Works on short text.
- Creates jointly embedded label, document, and word vectors.
Table of Contents
How does it work?
The key idea of the algorithm is that many semantically similar keywords can represent a topic. In the first step, the algorithm creates a joint embedding of document and word vectors. Once documents and words are embedded in a vector space, the goal of the algorithm is to learn label vectors from previously manually defined keywords representing a topic. Finally, the algorithm can predict the affiliation of documents to topics from document vector <-> label vector similarities.
The Algorithm
0. Use the manually defined keywords for each topic of interest.
Domain knowledge is needed to define keywords that describe topics and are semantically similar to each other within the topics.
| Basketball | Soccer | Baseball |
|---|---|---|
| NBA | FIFA | MLB |
| Basketball | Soccer | Baseball |
| LeBron | Messi | Ruth |
| ... | ... | ... |
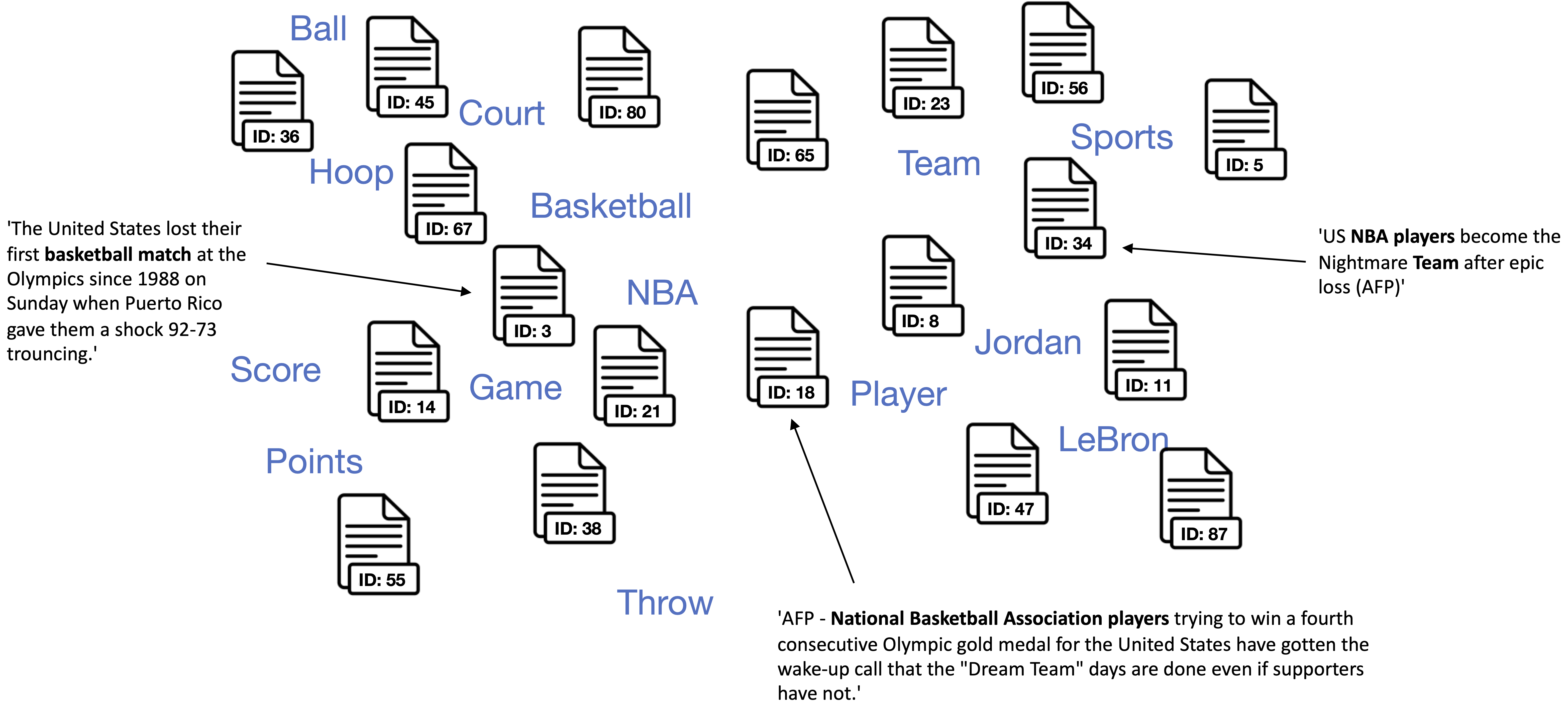
1. Create jointly embedded document and word vectors using Doc2Vec , Sentence-Transformers, or SimCSE.
Documents will be placed close to other similar documents and close to the most distinguishing words.
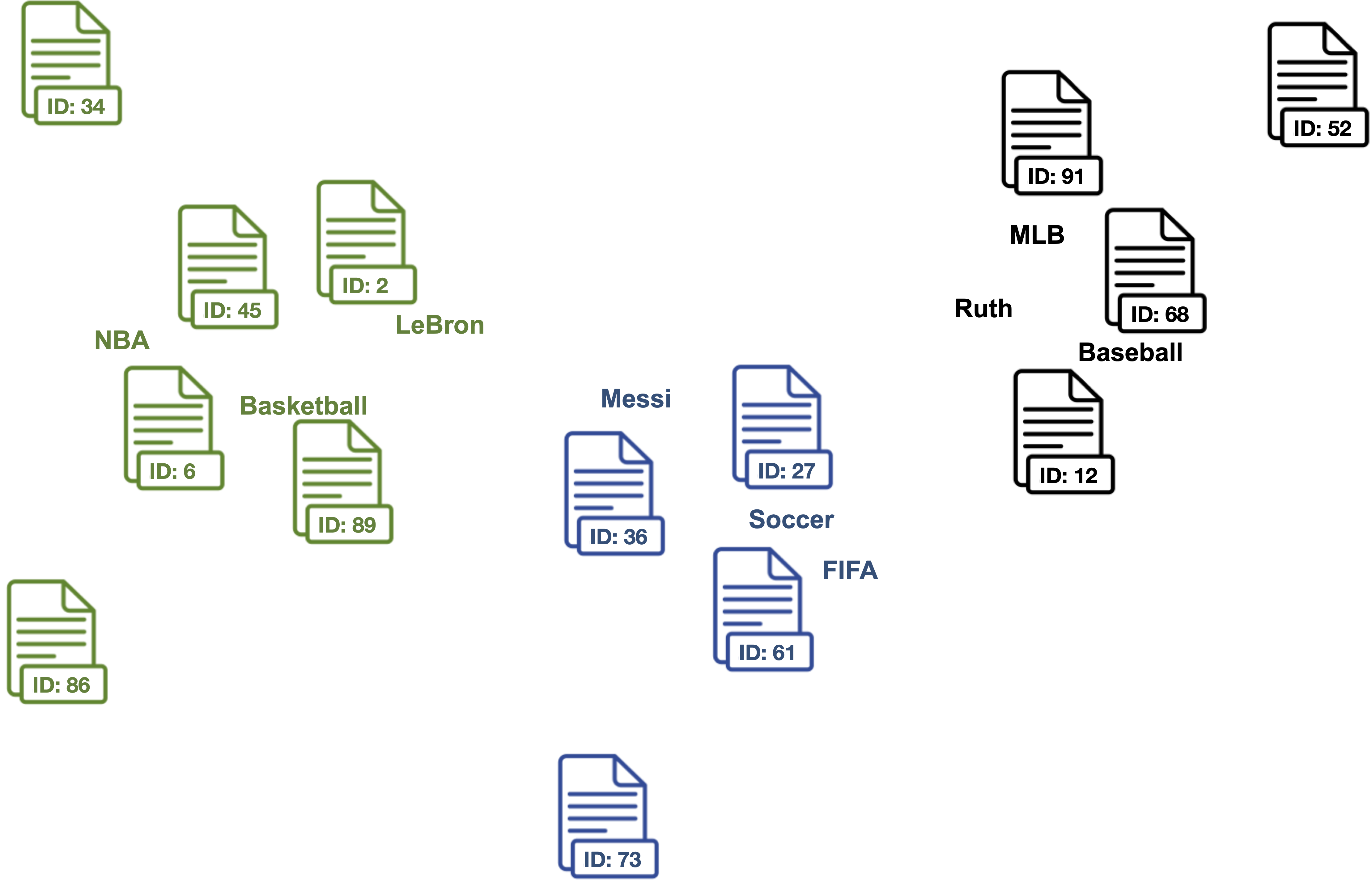
2. Find document vectors that are similar to the keyword vectors of each topic.
Each color represents a different topic described by the respective keywords.
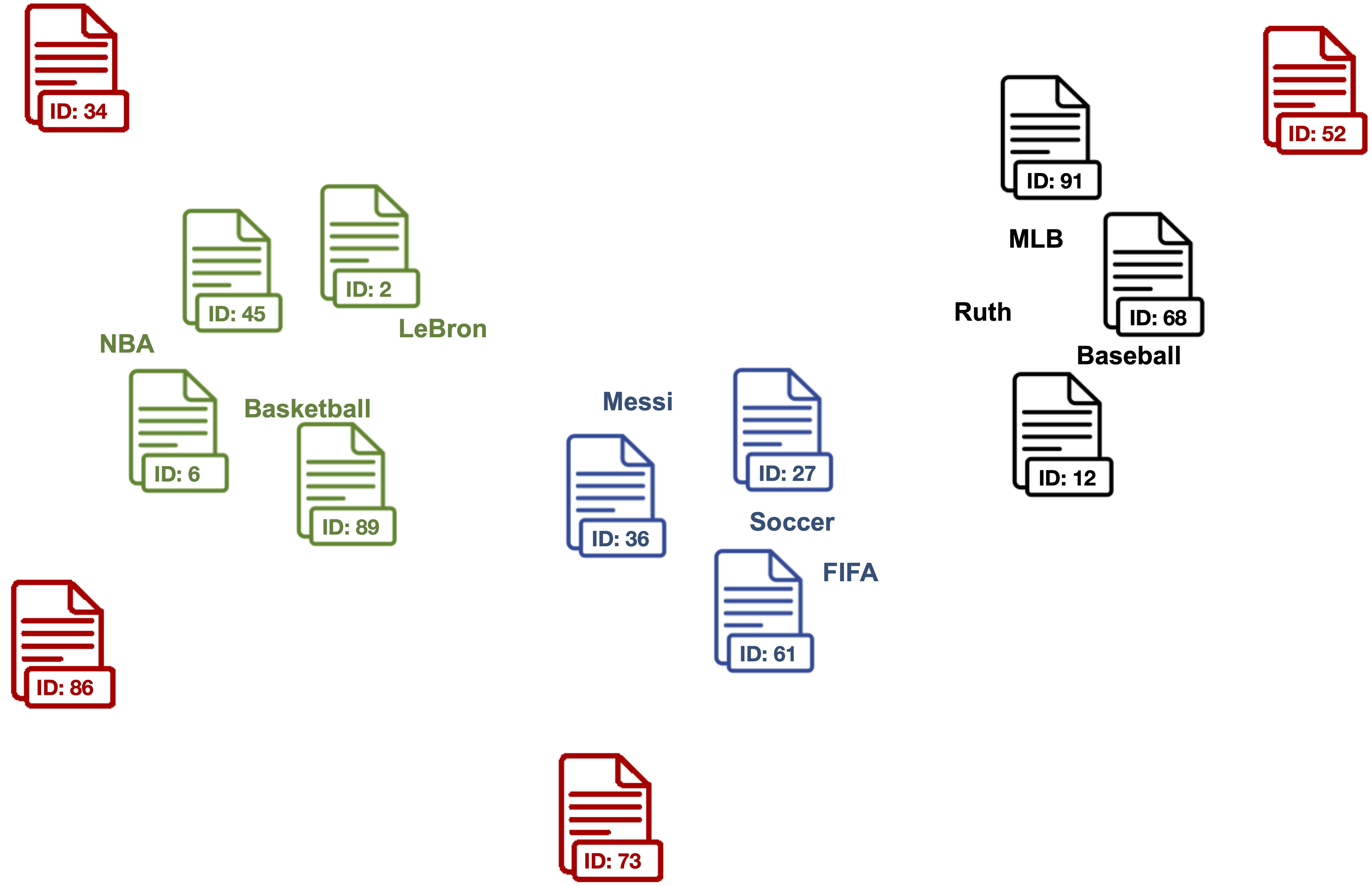
3. Clean outlier document vectors for each topic.
Red documents are outlier vectors that are removed and do not get used for calculating the label vector.
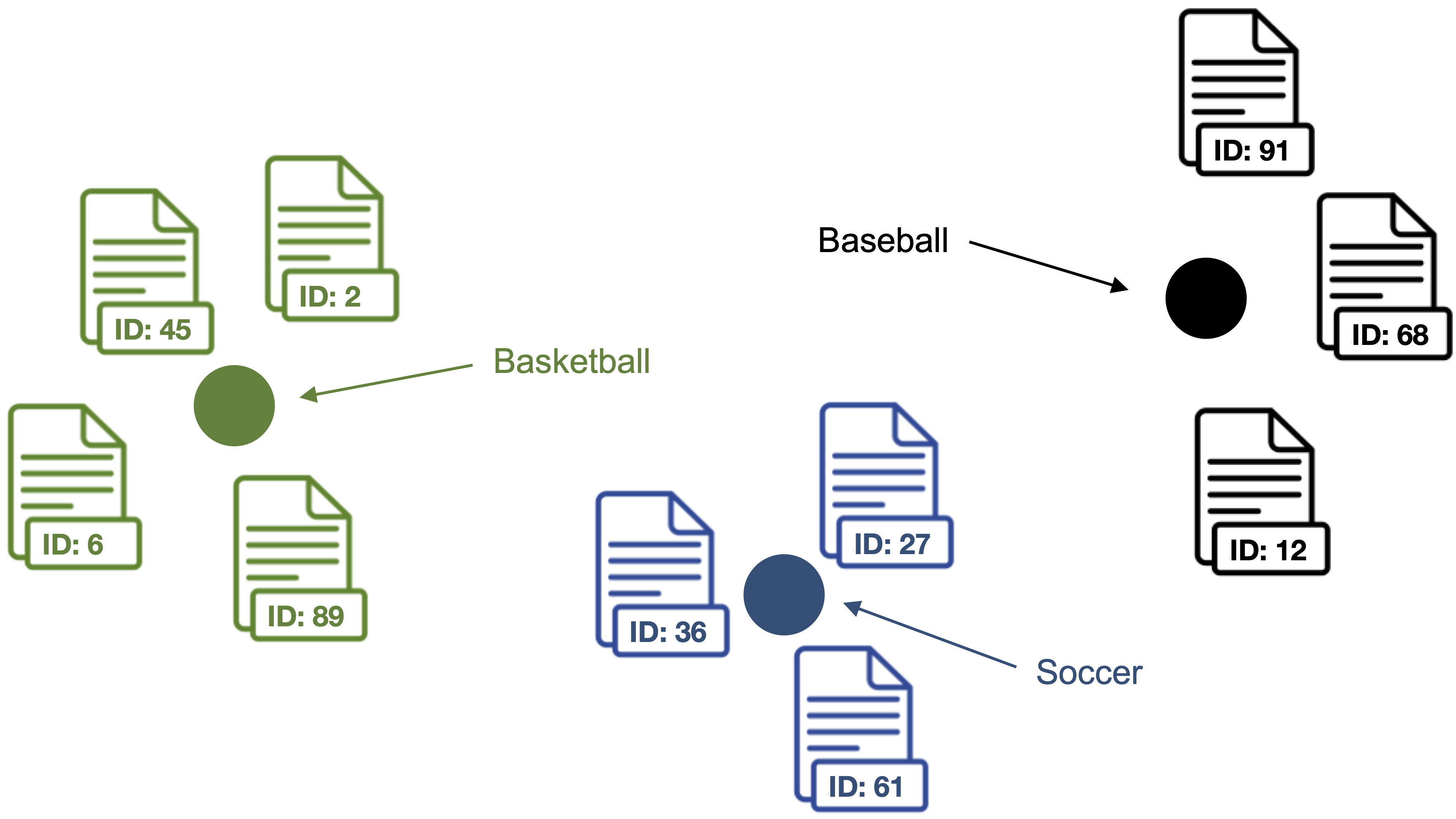
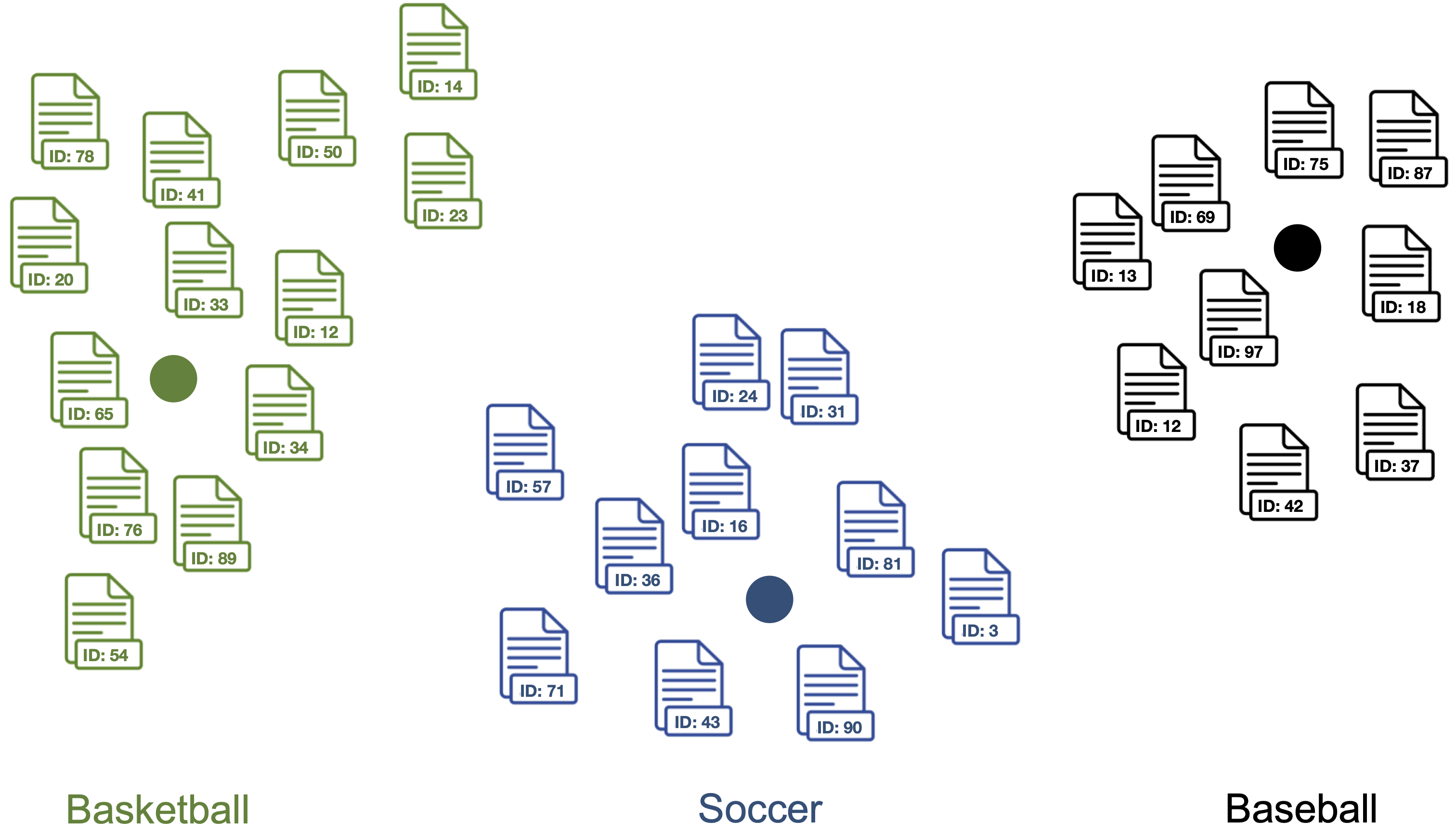
4. Compute the centroid of the outlier cleaned document vectors as label vector for each topic.
Points represent the label vectors of the respective topics.
5. Compute label vector <-> document vector similarities for each label vector and document vector in the dataset.
Documents are classified as topic with the highest label vector <-> document vector similarity.
Installation
pip install lbl2vec
Usage
For detailed information visit the API Guide and the examples.
Model Training
Lbl2Vec model
Lbl2Vec learns word vectors, document vectors and label vectors using Doc2Vec during training.
Train new Lbl2Vec model from scratch using Doc2Vec
from lbl2vec import Lbl2Vec
# init model
model = Lbl2Vec(keywords_list=descriptive_keywords, tagged_documents=tagged_docs)
# train model
model.fit()
Important parameters:
keywords_list: iterable list of lists with descriptive keywords of type str. For each label at least one descriptive keyword has to be added as list of str.tagged_documents: iterable list of gensim.models.doc2vec.TaggedDocument elements. If you wish to train a new Doc2Vec model this parameter can not be None, whereas thedoc2vec_modelparameter must be None. If you use a pretrained Doc2Vec model this parameter has to be None. Input corpus, can be simply a list of elements, but for larger corpora, consider an iterable that streams the documents directly from disk/network.
Use word and document vectors from pretrained Doc2Vec model
Uses word vectors and document vectors from a pretrained Doc2Vec model to learn label vectors during Lbl2Vec model training.
from lbl2vec import Lbl2Vec
# init model
model = Lbl2Vec(keywords_list=descriptive_keywords, doc2vec_model=pretrained_d2v_model)
# train model
model.fit()
Important parameters:
keywords_list: iterable list of lists with descriptive keywords of type str. For each label at least one descriptive keyword has to be added as list of str.doc2vec_model: pretrained gensim.models.doc2vec.Doc2Vec model. If given a pretrained Doc2Vec model, Lbl2Vec uses the pre-trained Doc2Vec model from this parameter. If this parameter is defined,tagged_documentsparameter has to be None. In order to get optimal Lbl2Vec results the given Doc2Vec model should be trained with the parameters "dbow_words=1" and "dm=0".
Lbl2TransformerVec model
Lbl2TransformerVec learns word vectors, document vectors and label vectors using transformer-based language models during training. Using state-of-the-art transformer embeddings may not only yield to better predictions but also eliminates the issue of unknown keywords during model training. While the Doc2Vec-based model can only use keywords that Lbl2Vec has seen during training, the transformer-based Lbl2TransformerVec model can learn label vectors from any set of keywords. That is because transformer vocabularies consist of individual characters, subwords, and words, allowing transformers to effectively represent every word in a sentence. This eliminates the out-of-vocabulary scenario. However, using transformers instead of Doc2Vec is much more computationally expensive, especially if no GPU is available.
Train new Lbl2TransformerVec model from scratch using the default transformer-embedding model
from lbl2vec import Lbl2TransformerVec
# init model using the default transformer-embedding model ("sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2")
model = Lbl2TransformerVec(keywords_list=listdescriptive_keywords, documents=document_list)
# train model
model.fit()
Train Lbl2TransformerVec model using an arbitrary Sentence-Transformers embedding model
from lbl2vec import Lbl2TransformerVec
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
# select sentence-tranformers model
transformer_model = SentenceTransformer("all-mpnet-base-v2")
# init model
model = Lbl2TransformerVec(transformer_model=transformer_model, keywords_list=listdescriptive_keywords,
documents=document_list)
# train model
model.fit()
Train Lbl2TransformerVec model using an arbitrary SimCSE embedding model
from lbl2vec import Lbl2TransformerVec
from transformers import AutoModel
# select SimCSE model
transformer_model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("princeton-nlp/sup-simcse-roberta-base")
# init model
model = Lbl2TransformerVec(transformer_model=transformer_model, keywords_list=listdescriptive_keywords,
documents=document_list)
# train model
model.fit()
Important parameters:
keywords_list: iterable list of lists with descriptive keywords of type str. For each label at least one descriptive keyword has to be added as list of str.documents: iterable list of text document elements (strings).transformer_model: Transformer model used to embed the labels, documents and keywords. The embedding models must be either of type sentence_transformers.SentenceTransformer or transformers.AutoModel
Document prediction
The prediction API calls are the same for Lbl2Vec and Lbl2TransformerVec.
Predict label similarities for documents used for training
Computes the similarity scores for each document vector stored in the model to each of the label vectors.
# get similarity scores from trained model
model.predict_model_docs()
Important parameters:
doc_keys: list of document keys (optional). If None: return the similarity scores for all documents that are used to train the Lbl2Vec model. Else: only return the similarity scores of training documents with the given keys.
Predict label similarities for new documents that are not used for training
Computes the similarity scores for each given and previously unknown document vector to each of the label vectors from the model.
# get similarity scores for each new document from trained model
model.predict_new_docs(tagged_docs=tagged_docs)
Important parameters:
tagged_docs: iterable list of gensim.models.doc2vec.TaggedDocument elements
Save and load models
The save and load API calls are the same for Lbl2Vec and Lbl2TransformerVec.
Save model to disk
model.save('model_name')
Load model from disk
model = Lbl2Vec.load('model_name')
Citation information
When citing Lbl2Vec or Lbl2TransformerVec in academic papers and theses, please use the following BibTeX entries:
@conference{schopf_etal_webist21,
author={Tim Schopf and Daniel Braun and Florian Matthes},
title={Lbl2Vec: An Embedding-based Approach for Unsupervised Document Retrieval on Predefined Topics},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - WEBIST,},
year={2021},
pages={124-132},
publisher={SciTePress},
organization={INSTICC},
doi={10.5220/0010710300003058},
isbn={978-989-758-536-4},
issn={2184-3252},
}
@inproceedings{schopf_etal_nlpir22,
author = {Schopf, Tim and Braun, Daniel and Matthes, Florian},
title = {Evaluating Unsupervised Text Classification: Zero-shot and Similarity-based Approaches},
year = {2023},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
booktitle = {2022 6th International Conference on Natural Language Processing and Information Retrieval (NLPIR)},
keywords = {Natural Language Processing, Unsupervised Text Classification, Zero-shot Text Classification},
location = {Bangkok, Thailand},
series = {NLPIR 2022}
}
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.