Tools to stream data to gephi
Project description
GephiStreamer
=============
Python classes for streaming graph to gephi
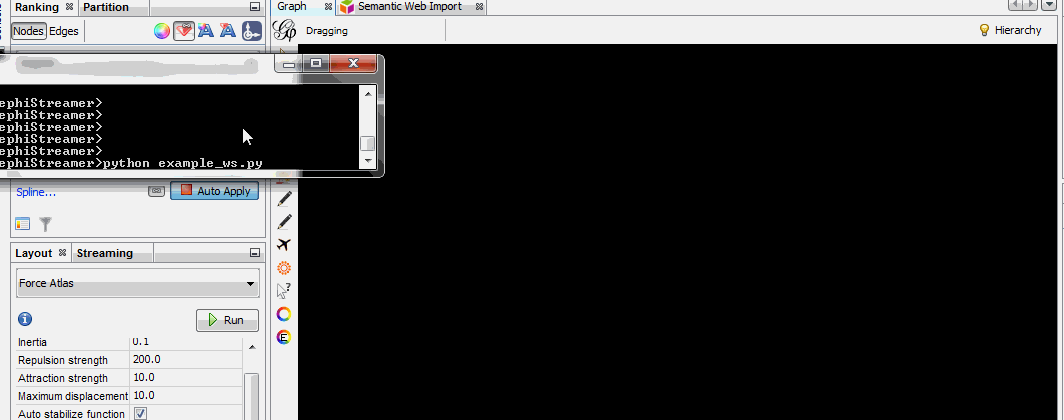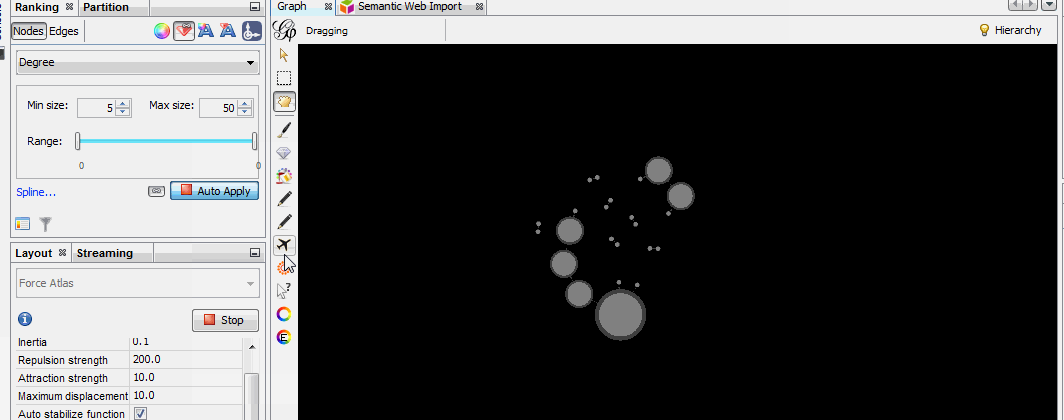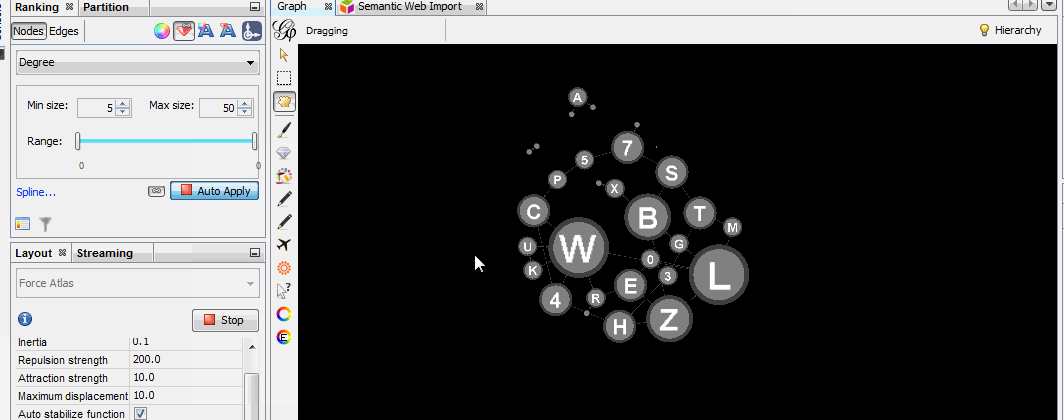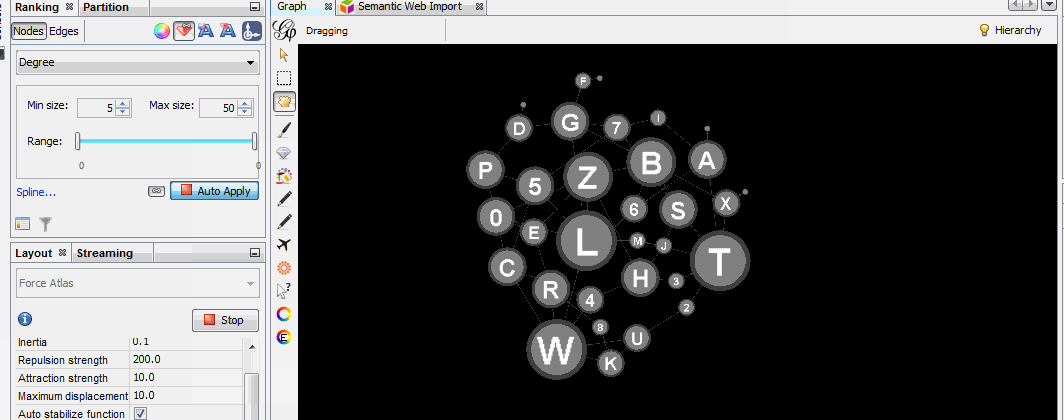
Install
======
`pip install gephistreamer`
Quick use
======
```python
# Basic import
from gephistreamer import graph
from gephistreamer import streamer
# Create a Streamer
# adapt if needed : streamer.GephiWS(hostname="localhost", port=8080, workspace="workspace0")
# You can also use REST call with GephiREST (a little bit slower than Websocket)
stream = streamer.Streamer(streamer.GephiWS())
# Create a node with a custom_property
node_a = graph.Node("A",custom_property=1)
# Create a node and then add the custom_property
node_b = graph.Node("B")
node_b.property['custom_property']=2
# Add the node to the stream
# you can also do it one by one or via a list
# l = [node_a,node_b]
# stream.add_node(*l)
stream.add_node(node_a,node_b)
# Create edge
# You can also use the id of the node : graph.Edge("A","B",custom_property="hello")
edge_ab = graph.Edge(node_a,node_b,custom_property="hello")
stream.add_edge(edge_ab)
```
How to
=====
Use the `Streamer` class to describe the action to perform:
* add_node
* change_node
* delete_node
* add_edge
* change_edge
* delete_edge
Don't forget to have Gephi running with the plugin [Graph Streaming](https://marketplace.gephi.org/plugin/graph-streaming/) installed and active in "Master mode".
GephiWS
=====
The GephiWS class communicates with Gephi as Websocket call.
GephiREST
=====
The GephiREST class communicates with Gephi as REST call.
Auto commit
=====
By default, all action will trigger a "commit" and send information to Gephi. You still
can use the old way by requiering a
```python
stream = streamer.Streamer(streamer.GephiREST(),auto_commit=False)
[.. actions ..]
stream.commit() # Will send all actions buffered to Gephi
```
=============
Python classes for streaming graph to gephi

Install
======
`pip install gephistreamer`
Quick use
======
```python
# Basic import
from gephistreamer import graph
from gephistreamer import streamer
# Create a Streamer
# adapt if needed : streamer.GephiWS(hostname="localhost", port=8080, workspace="workspace0")
# You can also use REST call with GephiREST (a little bit slower than Websocket)
stream = streamer.Streamer(streamer.GephiWS())
# Create a node with a custom_property
node_a = graph.Node("A",custom_property=1)
# Create a node and then add the custom_property
node_b = graph.Node("B")
node_b.property['custom_property']=2
# Add the node to the stream
# you can also do it one by one or via a list
# l = [node_a,node_b]
# stream.add_node(*l)
stream.add_node(node_a,node_b)
# Create edge
# You can also use the id of the node : graph.Edge("A","B",custom_property="hello")
edge_ab = graph.Edge(node_a,node_b,custom_property="hello")
stream.add_edge(edge_ab)
```
How to
=====
Use the `Streamer` class to describe the action to perform:
* add_node
* change_node
* delete_node
* add_edge
* change_edge
* delete_edge
Don't forget to have Gephi running with the plugin [Graph Streaming](https://marketplace.gephi.org/plugin/graph-streaming/) installed and active in "Master mode".

GephiWS
=====
The GephiWS class communicates with Gephi as Websocket call.
GephiREST
=====
The GephiREST class communicates with Gephi as REST call.
Auto commit
=====
By default, all action will trigger a "commit" and send information to Gephi. You still
can use the old way by requiering a
```python
stream = streamer.Streamer(streamer.GephiREST(),auto_commit=False)
[.. actions ..]
stream.commit() # Will send all actions buffered to Gephi
```










