A wrapper for Selenium to allow easy development of automated tests for the web
Project description




PySelenium
A Python package that uses Selenium to enable for automating tests for web applications.
Setup instructions
Get Google Chrome’s driver from https://sites.google.com/a/chromium.org/chromedriver/downloads
Put the web driver executable in any folder and add that folder to $PATH
Run pip install pyselenium
Usage
After successfully going through the setup instructions, you can start programming your tests like so:
from pyselenium.test_metadata import Test
from pyselenium.test_steps import *
from pyselenium.test_runner import *
test = Test('My test')
test.add_step(Navigate('http://www.google.com'))
test.add_step(TypeText(css_path='#lst-ib', hint='Google search bar', text='Automating a Google search'))
test.add_step(SendEnter())
test_runner = TestRunner(test)
test_result = test_runner.run_test()
print(test_result)Getting the CSS path from elements
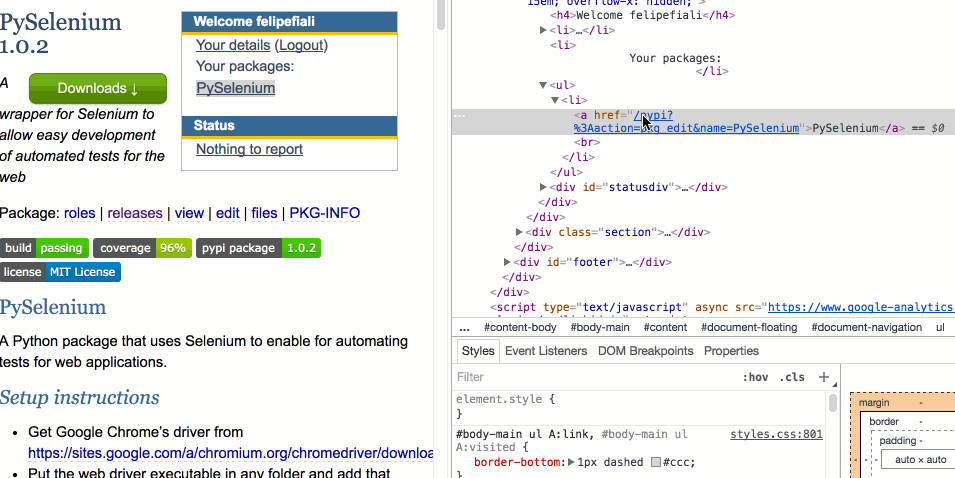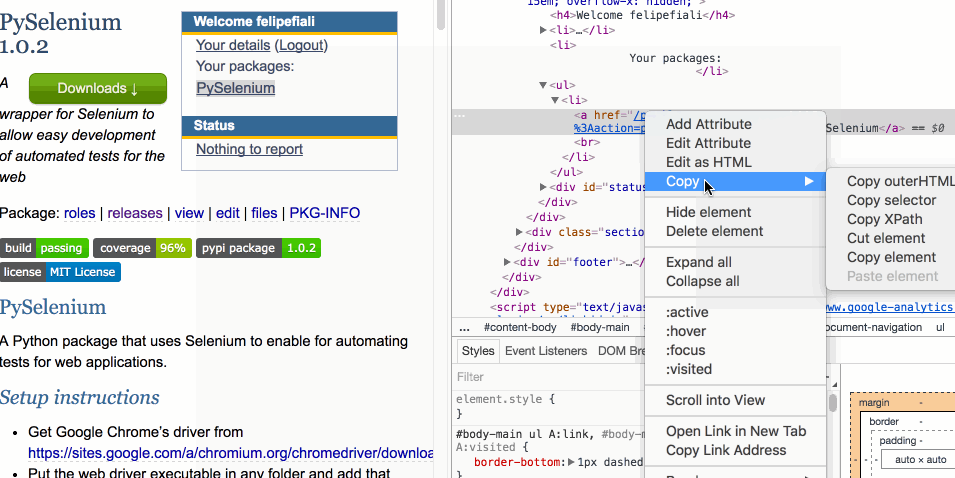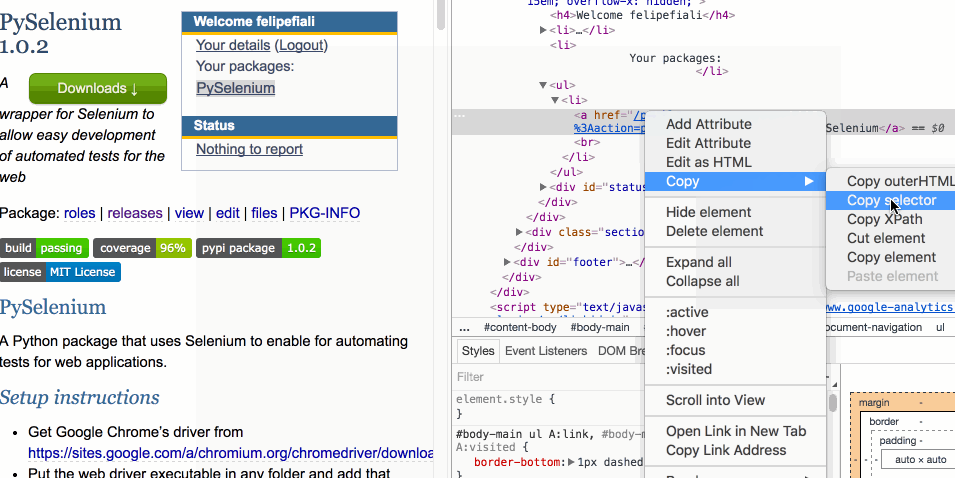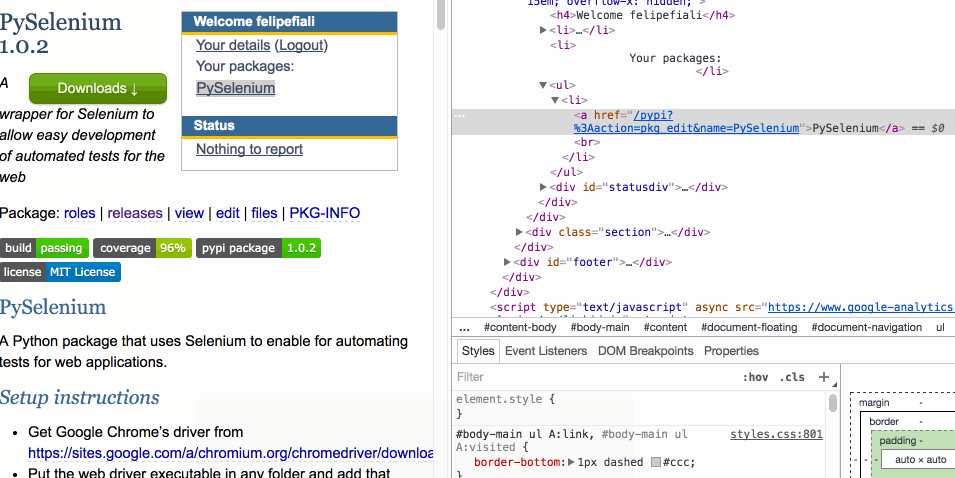
Finding the CSS path from elements is failry easy with Google Chrome. All you need to do is right-click the element, and hit “Inspect” to bring up the developer tools console:
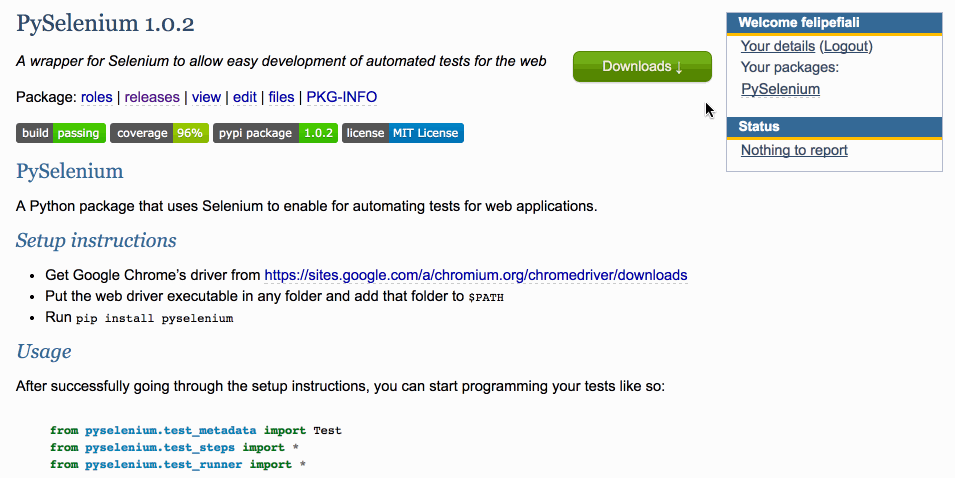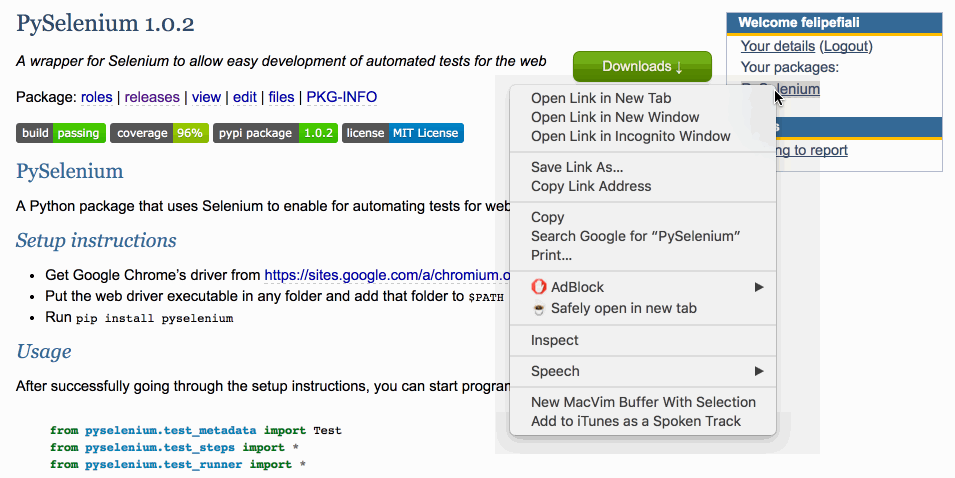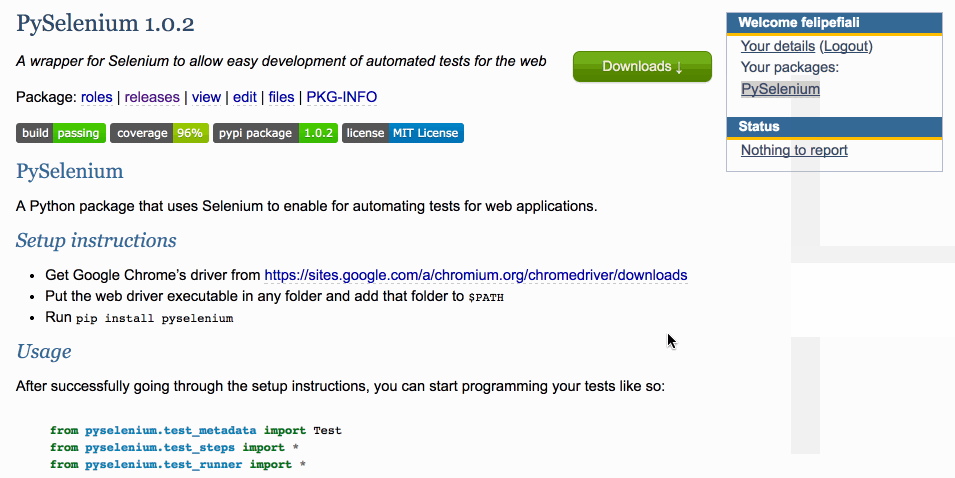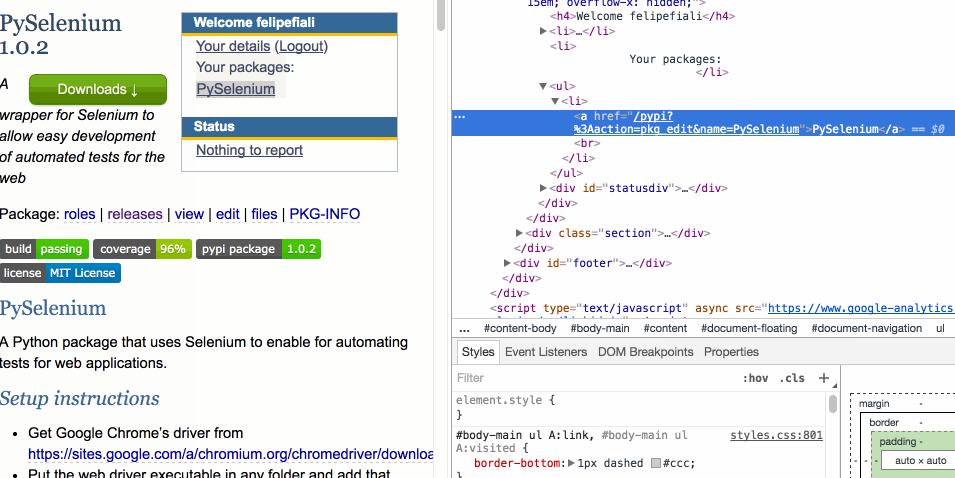
With the developer tools console opened, right-click the element in it and choose “Copy Selector”:
The CSS path of the selected element should already be in your clipboard after doing this.
Sample test
You can find a sample test in pyselenium/sample_test.py
List of available test steps
These are the test steps currently available to be used:
Navigate
Navigates to a specified URL.
Click
Clicks on a given element on the web page. It may be any HTML element. Fails if the element can not be found on the web page.
AssertElementValue
Asserts that the element value (text) is equal to the specified one. Fails if the found value is different from the expected one.
AssertElementAttributeValue
Asserts that the value of a specific attribute of the HTML element is equal to the specified one. Fails if the found value is different from the expected one.
ClickIfFound
Clicks on a given element on the web page. It may be any HTML element. Does not fail if the element can not be found on the web page. If the element is not found, does nothing.
AssertElementNotPresent
Asserts that an element is not present on the web page. Fails if the element is found.
TypeText
Simulates the user typing text on a given element on the web page. Fails if the element is not found.
SelectDropDownItemByText
Selects an option on a dropdown element by comparing its text to a given value. Fails if the element is not found.
SetCheckbox
Sets a checkbox to true or false. Fails if the checkbox is not found.
SwitchFrame
Switches the context to a given iFrame on the page. Fails if the iFrame is not found. After running this step, one should call the SwitchToDefaultContent right after running the needed steps on the selected iFrame to ensure that the context is switched back to the default content of the page.
SwitchToDefaultContent
Switches the context to the default content of the web page. Should always be called after switching the context to another iFrame and running the needed steps on that iFrame.
SendEnter
Sends an ENTER key to the webpage. It’s the same as if the user simply hit the return button on the keyboard. This step does not have any context information as to there the focus is on the page, so should only be used when necessary.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Hashes for PySelenium-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 7f6d1a1a731ade1eb1c65b0c259145b848499abadb8bf8389aedbef33c08ed17 |
|
| MD5 | c6ef7d9013945102e7650a9999f22867 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | d72e5d7db744c667f4bb11ac2e59acd7520cc15316d1b3e826f46c2c73f38874 |











