Flexible Lists of Values (LOV) for Django
Project description
flexible-list-of-values
Flexible and Extensible Lists of Values (LOV) for Django
When adding customizability to a SaaS app, there are a variety of approaches and tools:
- Dynamic models and dynamic model fields
- Entity-Attribute-Value (EAV)
- Adding JSONField to a model
But these approaches can be a bit too flexible. Sometimes we want to provide guardrails for our tenants.
flexible-list-of-values provides you a way to give your SaaS app's tenants customization options in its User-facing forms, but also lets you provide them with defaults - either mandatory or optional - to prevent each tenant having to "recreate the wheel".
Note: The terms "entity" and "tenant" are used interchangeably in this document to refer to a model within your project that has associated Users, and which has "ownership" over the LOV value options provided to its Users
Example implementation
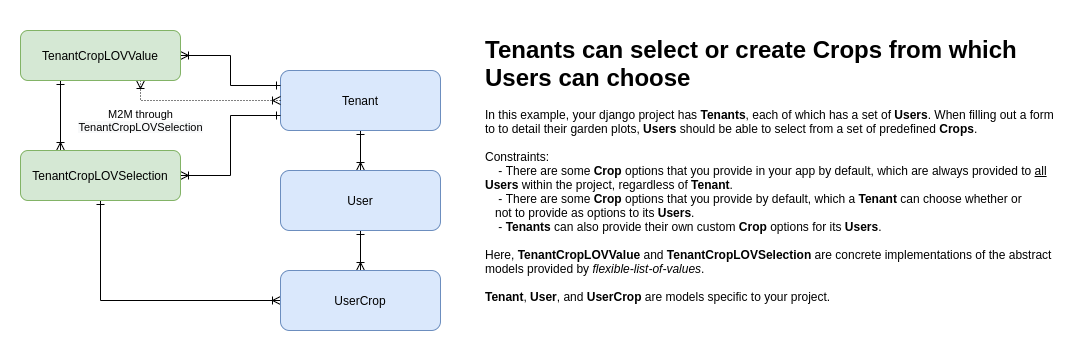
Imagine your project provides a form that allows your tenants' users provide details about their garden plots. Now you want to add a "crops" field to this form so that each tenants' users can also record the specific crops they are growing.
You could hard-code some crop value choices using CharField and choices, or if your tenants wanted the field to be customizable you could use JSONField or other methods, but this can get sloppy.
flexible-list-of-values provides an in-between option. You can specify some default options that are mandatory for all users, regardless of tenant, provide some default options that your tenants can either use or discard, and allow additional custom value options specific to the tenant and its users.
Docker Compose
This package comes with a demonstration project using docker compose. In order to utilize the project, we assume here that you have downloaded or cloned a copy of the project code repository, and that you already have docker compose installed. If not, see the compose docs.
Navigate to the "flexible-list-of-values" directory, and create a virtual environment to work from:
python3 -m venv .venv
Then activate the environment:
source .venv/bin/activate
Build the project:
docker compose build
Then run migrations and create a superuser.
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py createsuperuser
To synchronize the "lov_default" values with the database, run
python manage.py update_lovs
Bring the docker compose project up, where it will be available at http://127.0.0.1:8000/
docker compose up -d
Optionally create another user or two in admin
Within admin, create at least one tenant, setting the owner and users fields. The tenant owner can create new LOV Values and choose which Values its Users can select from.
If the user account you are logged in with is a tenant owner, then click here to add new LOV Values, or click here to specify which Values your users can choose from.
If the user account you are logged in with belongs to a tenant, then click here to choose from among the LOV Value choices the tenant has made available to you.
See the Test Project in the project repo for full details.
The Testapp Project
Here is what is going on behind the scenes.
models.py:
from django.contrib.auth import get_user_model
from django.db import models
from django.utils.translation import gettext_lazy as _
from flexible_list_of_values import LOVValueType
from flexible_list_of_values.models import AbstractLOVSelection, AbstractLOVValue
User = get_user_model()
class Tenant(models.Model):
"""
This model is a very simplistic example of how one might implement a Tenant architecture.
"""
name = models.CharField(_("Tenant Name"), max_length=100)
owner = models.ForeignKey(User, on_delete=models.CASCADE, related_name="owned_tenants", null=True, blank=True)
users = models.ManyToManyField(User, related_name="tenants", blank=True)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class TenantCropLOVValue(AbstractLOVValue):
"""
Concrete implementation of AbstractLOVValue with Crop options that a Tenant can modify.
"Fruit", "Herbs and Spices", and "Vegetable" are mandatory selections, but the others are provided to the Tenants as optional recommendations. Tenants can also add their own custom Values.
"""
lov_entity_model = "testapp.Tenant"
lov_selections_model = "testapp.TenantCropLOVSelection"
lov_defaults = {
"Fruit": {"value_type": LOVValueType.MANDATORY}, # 1
"Fruit - Apple": {"value_type": LOVValueType.OPTIONAL},
"Fruit - Mellon": {"value_type": LOVValueType.OPTIONAL},
"Fruit - Stone": {"value_type": LOVValueType.OPTIONAL},
"Herbs and Spices": {"value_type": LOVValueType.MANDATORY}, # 2
"Herbs and Spices - Basil": {"value_type": LOVValueType.OPTIONAL},
"Herbs and Spices - Sage": {"value_type": LOVValueType.OPTIONAL},
"Herbs and Spices - Thyme": {"value_type": LOVValueType.OPTIONAL},
"Vegetable": {"value_type": LOVValueType.MANDATORY}, # 3
"Vegetable - Avocado": {"value_type": LOVValueType.OPTIONAL},
"Vegetable - Cabbage": {"value_type": LOVValueType.OPTIONAL},
"Vegetable - Spinach": {"value_type": LOVValueType.OPTIONAL},
}
class Meta(AbstractLOVValue.Meta):
verbose_name = "Tenant Crop Value"
verbose_name_plural = "Tenant Crop Values"
ordering = ["name"]
class TenantCropLOVSelection(AbstractLOVSelection):
"""
Concrete implementation of AbstractLOVSelection with actual selections
of Crops that a Tenant's Users can select from in Forms
"""
lov_value_model = "testapp.TenantCropLOVValue"
lov_entity_model = "testapp.Tenant"
class Meta(AbstractLOVSelection.Meta):
verbose_name = "Tenant Crop Selection"
verbose_name_plural = "Tenant Crop Selections"
def __str__(self):
return self.lov_value.name
class UserCrop(models.Model):
"""
The crops which a User belonging to a particular Tenant has selected for their garden plot. (This is a very simplistic implementation of a Tenant-specific model and does not represent best practices.)
"""
user = models.ForeignKey(User, on_delete=models.CASCADE, related_name="user_crops")
tenant = models.ForeignKey(Tenant, on_delete=models.CASCADE, related_name="user_crops")
crops = models.ManyToManyField(TenantCropLOVValue)
For the example above, in a UserCrop form for Users of TenantA or TenantB ...
- The
cropsModelChoiceField will always include Crop choices for "Fruit", "Herbs and Spices", and "Vegetable". - Both tenants can choose whether their Users will have the other values listed in
lov_defaults. - And both tenants can create custom tenant-specific value options for their Users to choose from.
Working with LOV Values
View the available Values for this Tenant:
tenant = Tenant.objects.first()
values_for_tenant = TenantCropLOVValue.objects.for_entity(tenant)
Alternately:
tenant = Tenant.objects.first()
values_for_tenant = TenantCropLOVSelection.objects.values_for_entity(tenant)
View the selected Values for this Tenant:
tenant = Tenant.objects.first()
selected_values_for_entity = TenantCropLOVSelection.objects.selected_values_for_entity(tenant)
Create new custom Values for this Tenant:
tenant = Tenant.objects.first()
TenantCropLOVValue.objects.create_for_entity(tenant, "New Value for this Tenant")
Delete Values for this Tenant (only deletes custom values owned by this tenant)
tenant = Tenant.objects.first()
values = TenantCropLOVValue.objects.for_entity(entity=tenant).filter(name__icontains="Something")
for value in values:
value.delete()
Letting tenants select LOV value choices for their users
Tenants can select from among the Values available for this Tenant or create new Values
forms.py:
from django import forms
from flexible_list_of_values.forms import (
LOVValueCreateFormMixin,
LOVSelectionsModelForm,
)
from tests.testapp.models import TenantCropLOVSelection, TenantCropLOVValue
class TenantCropValueCreateForm(LOVValueCreateFormMixin, forms.ModelForm):
"""
Form to let a tenant add a new custom LOV Value.
"""
class Meta:
model = TenantCropLOVValue
fields = ["name", "lov_entity", "value_type"]
class TenantCropValueSelectionForm(LOVSelectionsModelForm):
"""
Form to let a tenant select which LOV Values its users can choose from.
"""
class Meta:
model = TenantCropLOVSelection
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.fields["lov_selections"].widget.attrs["size"] = "10"
views.py
from django.template.response import TemplateResponse
from tests.testapp.models import TenantCropLOVValue
from tests.testapp.forms import TenantCropValueCreateForm, TenantCropValueSelectionForm
# Add decorator or other logic to allow only logged in tenant owners access to this view
def lov_crop_value_create_view(request):
"""
Form for creating new values for a Tenant
"""
template = "testapp/create_value.html"
context = {}
# However you specify the current entity/tenant for the User submitting this form.
# This is only an example.
tenant = request.user.owned_tenants.first()
# Here we provide the User's entity, which the form will use to determine the available Values
form = TenantCropValueCreateForm(request.POST or None, lov_entity=tenant)
if request.method == "POST":
if form.is_valid():
form.save()
context["form"] = form
# Provide the list of existing LOV Values for this Tenant
context["existing_values"] = TenantCropLOVValue.objects.for_entity(tenant)
return TemplateResponse(request, template, context)
# Add decorator or other logic to allow only logged in tenant owners access to this view
def lov_tenant_crop_selection_view(request):
"""
Form for selecting the Values a tenant wants to use
"""
template = "testapp/select_values.html"
context = {}
# However you specify the current entity/tenant for the User submitting this form.
# This is only an example.
tenant = request.user.owned_tenants.first()
# Here we provide the entity
form = TenantCropValueSelectionForm(request.POST or None, lov_entity=tenant)
if request.method == "POST":
if form.is_valid():
form.save()
# Update form's contents to ensure mandatory items are selected
form = TenantCropValueSelectionForm(None, lov_entity=tenant)
context["form"] = form
return TemplateResponse(request, template, context)
Working with a tenant's LOV Selections
A Tenant's Users make a choice from among the selected Values for this Tenant each time they fill out a UserCrop Selection Form.
forms.py (continued from previous forms.py code):
from django import forms
from tests.testapp.models import UserCrop
class UserCropSelectionForm(forms.ModelForm):
"""
Form to let a Tenant's Users select from available LOV Values.
"""
class Meta:
model = UserCrop
fields = "__all__"
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
self.user = kwargs.pop("user", None)
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
# Get all allowed values for this tenant
if self.instance:
self.fields["crops"].queryset = TenantCropLOVSelection.objects.selections_for_entity(self.instance.tenant)
self.fields["user"].initial = self.user
self.fields["tenant"].initial = self.instance.tenant
else:
self.fields["crops"].queryset = TenantCropLOVSelection.objects.none()
self.fields["crops"].widget.attrs["size"] = "10"
views.py (continued from previous views.py code):
from django.template.response import TemplateResponse
from tests.testapp.models import UserCrop
from tests.testapp.forms import UserCropSelectionForm
# Add decorator or other logic to allow only logged in users who belong to a tenant to access to this view
def lov_user_crop_selection_view(request):
"""
A for that allows a Tenant's Users to select the Crops they want to select
"""
template = "testapp/select_values.html"
context = {}
# However you specify the current entity/tenant for the User submitting this form.
# This is only an example.
tenant = request.user.tenants.first()
obj = obj, created = UserCrop.objects.get_or_create(
user=request.user,
tenant=tenant,
)
# Here we provide the entity
form = UserCropSelectionForm(request.POST or None, instance=obj)
if request.method == "POST":
if form.is_valid():
form.save()
context["form"] = form
return TemplateResponse(request, template, context)
Here, Users for TenantA who are filling out a UserCropSelectionForm form will see all mandatory values, the optional values that TenantA has selected, and any custom values TenantA has created. TenantB's users will see all mandatory values, the optional values that TenantB has selected, and any custom values TenantB has created.
Management Commands
update_lovs: Synchronizes thelov_defaultsin each model, if any, with the database.
API
Model: AbstractLOVValue
Fields
- id: default id
- name (CharField): The name or title of the value to be used.
- lov_entity (FK): the owning entity for this value. If this is a default value, this field will be null.
- lov_associated_entities (M2M): all entities this value is associated with. (The reverse relationship on the entity model is all values selected for the entity)
- value_type (CharField): Any of
- LOVValueType.MANDATORY
- LOVValueType.OPTIONAL
- LOVValueType.CUSTOM
- deleted (DateTimeField): The datetime this value was deleted, or null if it is not deleted.
Model attributes
- lov_defaults
-
A dictionary of default mandatory and optional values from which an entity can select. See usage examples above.
Default:{} - lov_entity_model
-
Specifies the model class for the 'entity' in your project which can customize its Users' LOVs. Specify the string representation of the model class (e.g.:
"entities.Entity").
* Required - lov_entity_on_delete
-
What should happen when the related entity instance is deleted.
Default:models.CASCADE - lov_entity_model_related_name
-
related_namefor the related entity instance.
Default:"%(app_label)s_%(class)s_related" - lov_entity_model_related_query_name
-
related_query_namefor the related entity instance.
Default:"%(app_label)s_%(class)ss" - lov_selections_model
-
Specifies the model class of the through-model between an Entity and a Value. Each instance of this through-model is an option that the tenant's users can choose from. Must be a concrete subclass of AbstractLOVSelection. Specify the string representation of the model class (e.g.:
"entities.TenantCropLOVSelection").
* Required - lov_associated_entities_related_name
-
related_namefor the M2M to the entity instance.
Default:"%(app_label)s_%(class)s_related" - lov_associated_entities_related_query_name
-
related_query_namefor the M2M to the entity instance.
Default:"%(app_label)s_%(class)ss"
Manager and QuerySet Methods
- for_entity(entity)
-
Returns QuerySet of all available values for a given entity, including:
- all required default values
- all non-required default values
- all entity-specific values for this entity
- create_for_entity(entity, name: str)
- Creates a new selectable Value for the provided entity.
- create_mandatory(name: str)
- Creates a new Value (selected for all entities).
- create_optional(name: str)
- Creates a new selectable optional Value (selectable by all entities).
Model: AbstractLOVSelection
This is a through-model from an concrete LOVValue model instance to an entity model instance representing the value selections an entity has made.
Fields
- id: default id
- lov_entity (FK): the entity this selection is associated with.
- lov_value (FK): the value this selection is associated with.
Model attributes
- lov_entity_model
-
Specifies the model class for the 'entity' in your project which can customize its Users' LOVs. Specify the string representation of the model class (e.g.:
"entities.Entity").
* Required - lov_entity_on_delete
-
What should happen when the related entity instance is deleted.
Default:models.CASCADE - lov_entity_model_related_name
-
related_namefor the related entity instance.
Default:"%(app_label)s_%(class)s_related" - lov_entity_model_related_query_name
-
related_query_namefor the related entity instance.
Default:"%(app_label)s_%(class)ss" - lov_value_model
-
Specifies the model class for the concrete (not abstract!) subclass of AbstractLOVValue. Specify the string representation of the model class (e.g.:
"contacts.TenantCropLOVSelection").
* Required - lov_value_model_related_name
-
related_namefor the related concrete subclassed AbstractLOVValue instance.
Default:"%(app_label)s_%(class)s_related" - lov_value_model_related_query_name
-
related_query_namefor the related concrete subclassed AbstractLOVValue instance.
Default:"%(app_label)s_%(class)ss"
Manager and QuerySet Methods
- values_for_entity(entity)
-
Returns QuerySet of all available values for a given entity, including:
- all required default values
- all non-required default values
- all entity-specific values for this entity
- selected_values_for_entity(entity)
-
Returns QuerySet of all selected values for a given entity, including:
- all required default values
- all selected non-required default values
- all selected entity-specific values for this entity
Project details
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Hashes for flexible_list_of_values-0.2.0.tar.gz
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 85b6b710bf1f7a8288235159e4c73ce139f3c89ab59a9937df9ca2fd044f39cb |
|
| MD5 | 8bf56e35e80013ddf2a9ff5b16b73615 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | e17687a015c4a2d614cebd264c6d812a82c945f9664dd59fce95277cf6fbec4d |
Hashes for flexible_list_of_values-0.2.0-py3-none-any.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 2cdec505a8eafaabb62d3598c0066cc81b6b397cb3e90585ecee105457136d31 |
|
| MD5 | ab9e33497b9b285946b1aa70385ff375 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 44a060f4b270ecf92b2486e800cdafce74c34c6b3de568ee46e566a40610aa8e |