AgileRL is a deep reinforcement learning library focused on improving RL development through RLOps.
Project description
AgileRL

Reinforcement learning streamlined.
Easier and faster reinforcement learning with RLOps. Visit our website. View documentation.
Join the Discord Server to collaborate.
NEW: AgileRL now supports custom network architectures and pre-trained models with the new MakeEvolvable wrapper!
This is a Deep Reinforcement Learning library focused on improving development by introducing RLOps - MLOps for reinforcement learning.
This library is initially focused on reducing the time taken for training models and hyperparameter optimization (HPO) by pioneering evolutionary HPO techniques for reinforcement learning.
Evolutionary HPO has been shown to drastically reduce overall training times by automatically converging on optimal hyperparameters, without requiring numerous training runs.
We are constantly adding more algorithms and features. AgileRL already includes state-of-the-art evolvable on-policy, off-policy, offline and multi-agent reinforcement learning algorithms with distributed training.
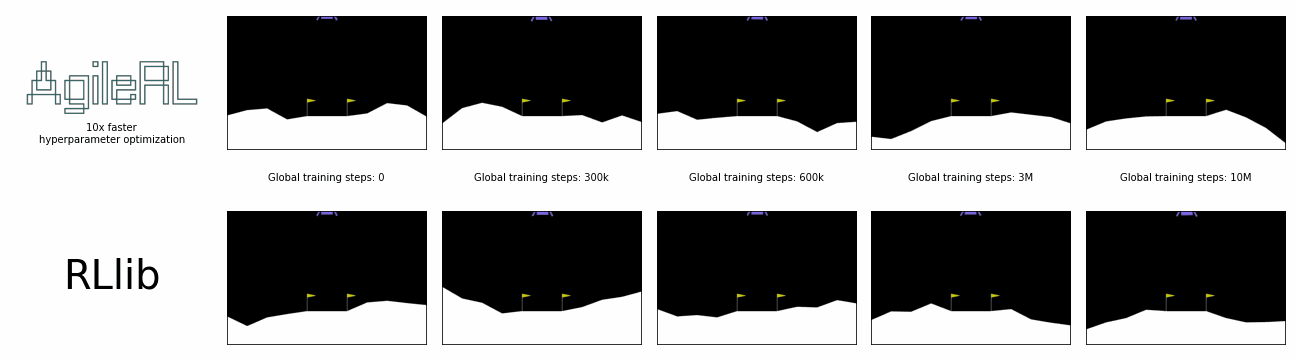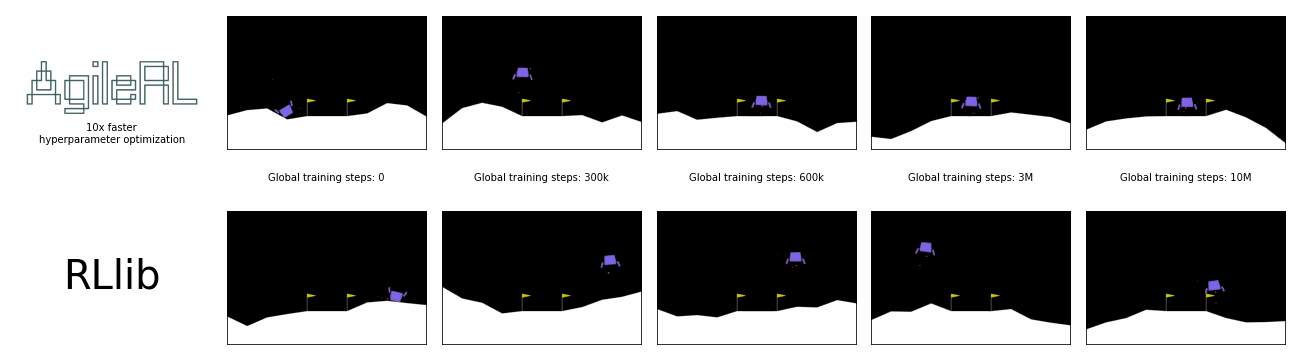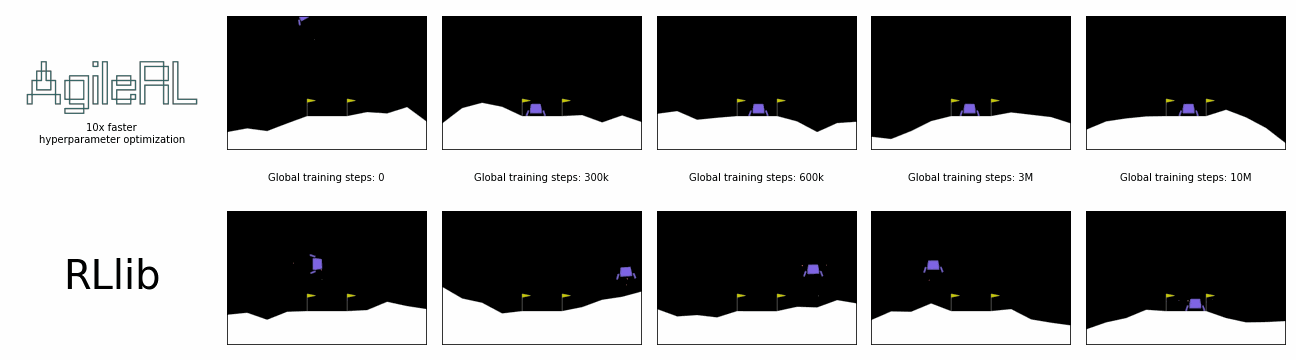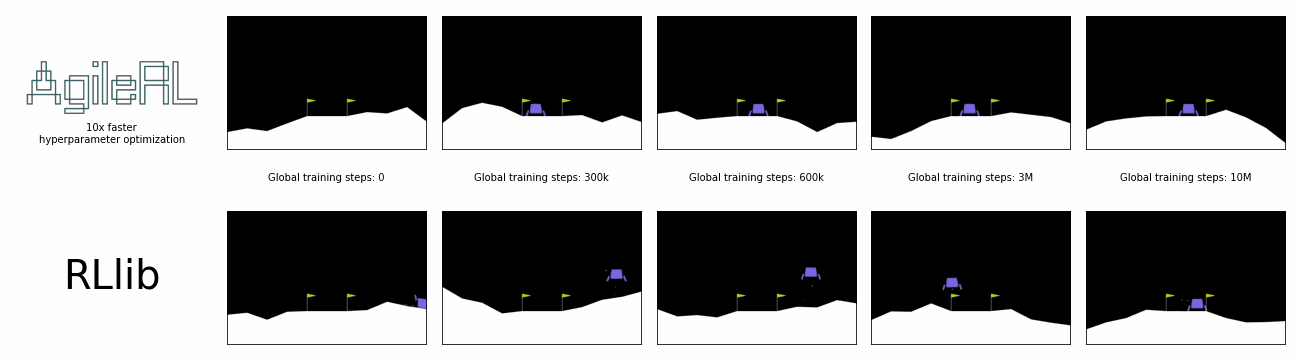
AgileRL offers 10x faster hyperparameter optimization than SOTA.
Global steps is the sum of every step taken by any agent in the environment, including across an entire population, during the entire hyperparameter optimization process.
Table of Contents
- Benchmarks
- Get Started
- Tutorials
- Algorithms implemented
- Train an agent on a Gym environment (Online)
- Train an agent on data (Offline)
- Train an agent on a language environment (RLHF)
- Distributed training
- Multi-agent training
Benchmarks
Reinforcement learning algorithms and libraries are usually benchmarked once the optimal hyperparameters for training are known, but it often takes hundreds or thousands of experiments to discover these. This is unrealistic and does not reflect the true, total time taken for training. What if we could remove the need to conduct all these prior experiments?
In the charts below, a single AgileRL run, which automatically tunes hyperparameters, is benchmarked against Optuna's multiple training runs traditionally required for hyperparameter optimization, demonstrating the real time savings possible. Global steps is the sum of every step taken by any agent in the environment, including across an entire population.
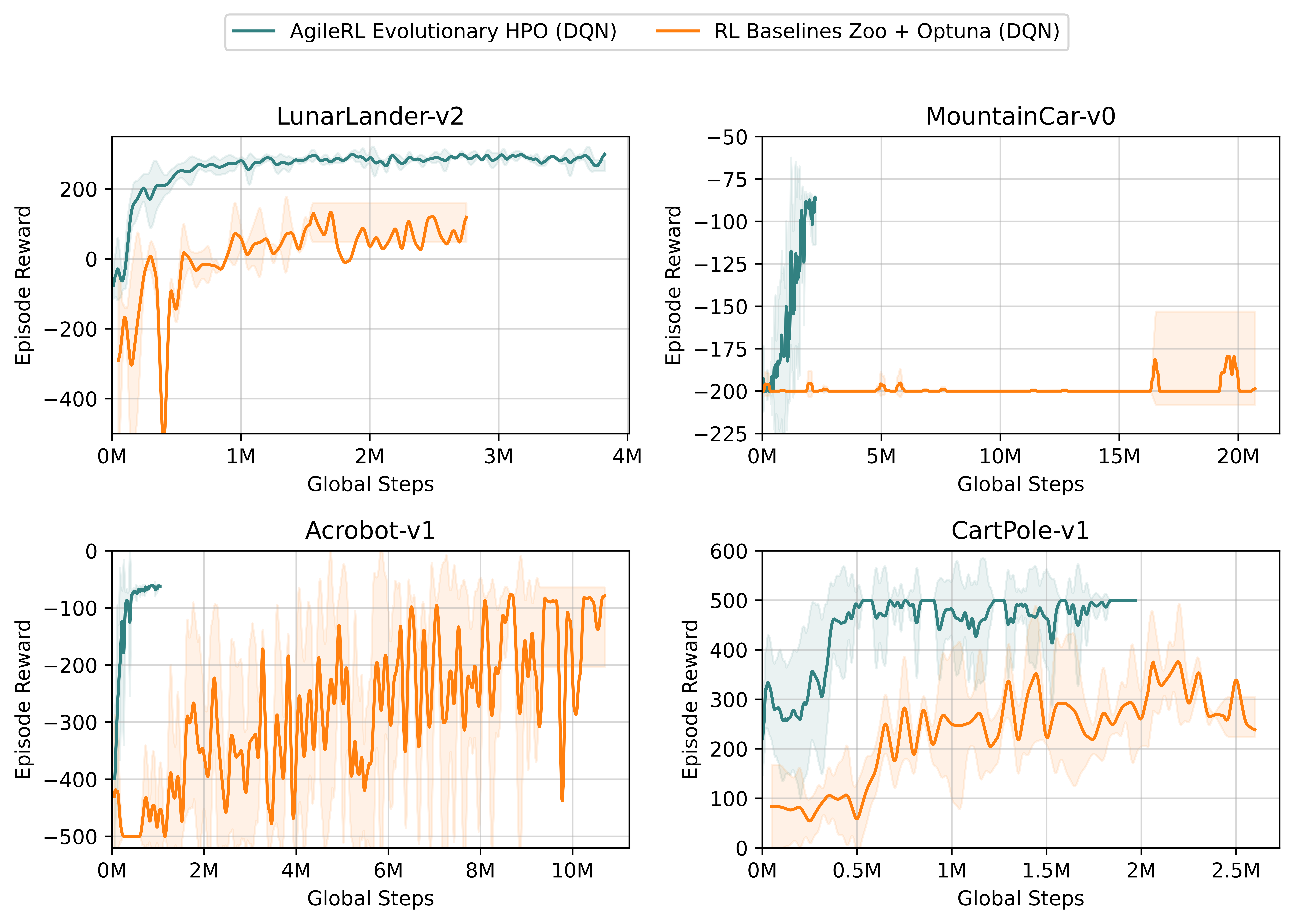
AgileRL offers an order of magnitude speed up in hyperparameter optimization vs popular reinforcement learning training frameworks combined with Optuna. Remove the need for multiple training runs and save yourself hours.
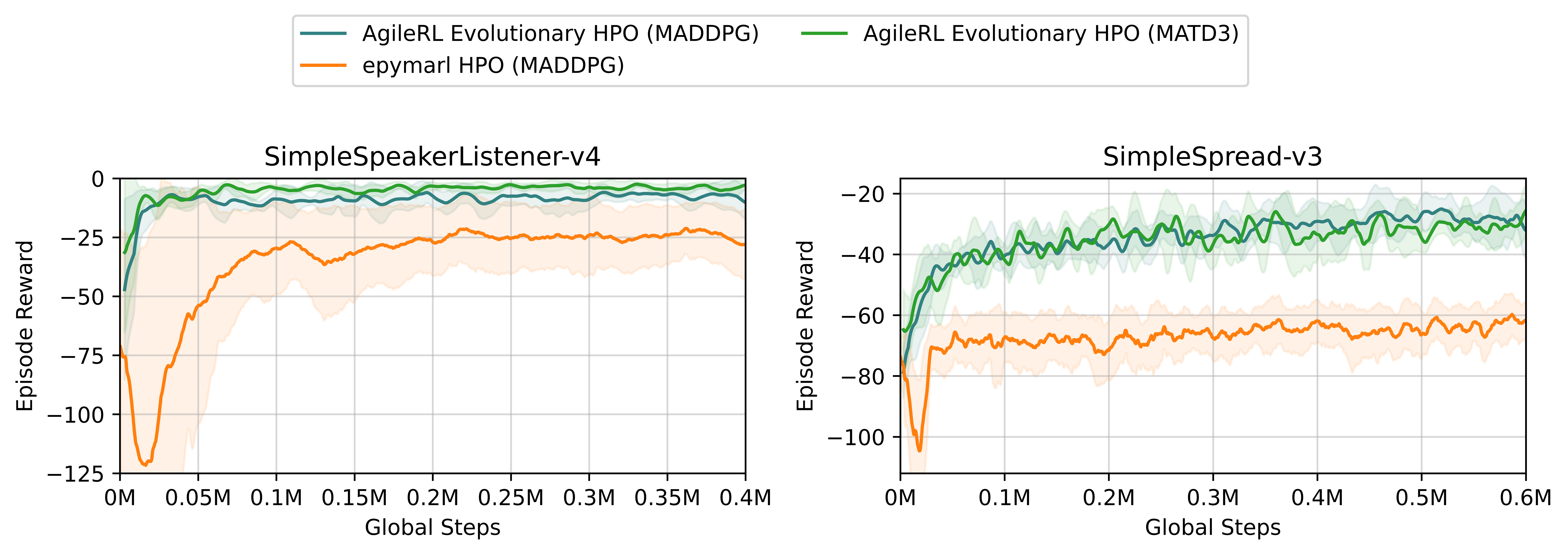
AgileRL also supports multi-agent reinforcement learning using the Petting Zoo-style (parallel API). The charts below highlight the performance of our MADDPG and MATD3 algorithms with evolutionary hyper-parameter optimisation (HPO), benchmarked against epymarl's MADDPG algorithm with grid-search HPO for the simple speaker listener and simple spread environments.
Get Started
Install as a package with pip:
pip install agilerl
Or install in development mode: (Recommended due to nascent nature of this library)
git clone https://github.com/AgileRL/AgileRL.git && cd AgileRL
pip install -r requirements.txt
If using ILQL on Wordle, download and unzip data.zip here.
Demo:
cd demos
python demo_online.py
or to demo distributed training:
cd demos
accelerate launch --config_file configs/accelerate/accelerate.yaml demos/demo_online_distributed.py
Note: If you are running demo or benchmarking scripts in development mode, without having installed AgileRL, you will need to uncomment two lines at the beginning of the file.
Tutorials
We are in the process of creating tutorials on how to use AgileRL and train agents on a variety of tasks. Currently, we have tutorials for single-agent tasks, such as training DQN to play Connect Four with curriculum learning and self-play, and also for multi-agent tasks in MPE environments. Check them out in our docs here. Our demo files also provide examples on how to train agents using AgileRL, and more information can be found in our documentation.
Evolvable algorithms implemented (more coming soon!)
- DQN
- Rainbow DQN
- DDPG
- PPO
- CQL
- ILQL
- TD3
- MADDPG
- MATD3
Train an agent on a Gym environment (Online)
Off-policy Reinforcement Learning
Before starting training, there are some meta-hyperparameters and settings that must be set. These are defined in INIT_HP, for general parameters, and MUTATION_PARAMS, which define the evolutionary probabilities, and NET_CONFIG, which defines the network architecture. For example:
INIT_HP = {
'ENV_NAME': 'LunarLander-v2', # Gym environment name
'ALGO': 'DQN', # Algorithm
'DOUBLE': True, # Use double Q-learning
'CHANNELS_LAST': False, # Swap image channels dimension from last to first [H, W, C] -> [C, H, W]
'BATCH_SIZE': 256, # Batch size
'LR': 1e-3, # Learning rate
'EPISODES': 2000, # Max no. episodes
'TARGET_SCORE': 200., # Early training stop at avg score of last 100 episodes
'GAMMA': 0.99, # Discount factor
'MEMORY_SIZE': 10000, # Max memory buffer size
'LEARN_STEP': 1, # Learning frequency
'TAU': 1e-3, # For soft update of target parameters
'TOURN_SIZE': 2, # Tournament size
'ELITISM': True, # Elitism in tournament selection
'POP_SIZE': 6, # Population size
'EVO_EPOCHS': 20, # Evolution frequency
'POLICY_FREQ': 2, # Policy network update frequency
'WANDB': True # Log with Weights and Biases
}
MUTATION_PARAMS = {
# Relative probabilities
'NO_MUT': 0.4, # No mutation
'ARCH_MUT': 0.2, # Architecture mutation
'NEW_LAYER': 0.2, # New layer mutation
'PARAMS_MUT': 0.2, # Network parameters mutation
'ACT_MUT': 0, # Activation layer mutation
'RL_HP_MUT': 0.2, # Learning HP mutation
'RL_HP_SELECTION': ['lr', 'batch_size'], # Learning HPs to choose from
'MUT_SD': 0.1, # Mutation strength
'RAND_SEED': 1, # Random seed
}
NET_CONFIG = {
'arch': 'mlp', # Network architecture
'h_size': [32, 32], # Actor hidden size
}
First, use utils.utils.initialPopulation to create a list of agents - our population that will evolve and mutate to the optimal hyperparameters.
from agilerl.utils.utils import makeVectEnvs, initialPopulation
import torch
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
env = makeVectEnvs(env_name=INIT_HP['ENV_NAME'], num_envs=16)
try:
state_dim = env.single_observation_space.n # Discrete observation space
one_hot = True # Requires one-hot encoding
except Exception:
state_dim = env.single_observation_space.shape # Continuous observation space
one_hot = False # Does not require one-hot encoding
try:
action_dim = env.single_action_space.n # Discrete action space
except Exception:
action_dim = env.single_action_space.shape[0] # Continuous action space
if INIT_HP['CHANNELS_LAST']:
state_dim = (state_dim[2], state_dim[0], state_dim[1])
agent_pop = initialPopulation(algo=INIT_HP['ALGO'], # Algorithm
state_dim=state_dim, # State dimension
action_dim=action_dim, # Action dimension
one_hot=one_hot, # One-hot encoding
net_config=NET_CONFIG, # Network configuration
INIT_HP=INIT_HP, # Initial hyperparameters
population_size=INIT_HP['POP_SIZE'], # Population size
device=device)
Next, create the tournament, mutations and experience replay buffer objects that allow agents to share memory and efficiently perform evolutionary HPO.
from agilerl.components.replay_buffer import ReplayBuffer
from agilerl.hpo.tournament import TournamentSelection
from agilerl.hpo.mutation import Mutations
field_names = ["state", "action", "reward", "next_state", "done"]
memory = ReplayBuffer(action_dim=action_dim, # Number of agent actions
memory_size=INIT_HP['MEMORY_SIZE'], # Max replay buffer size
field_names=field_names, # Field names to store in memory
device=device)
tournament = TournamentSelection(tournament_size=INIT_HP['TOURN_SIZE'], # Tournament selection size
elitism=INIT_HP['ELITISM'], # Elitism in tournament selection
population_size=INIT_HP['POP_SIZE'], # Population size
evo_step=INIT_HP['EVO_EPOCHS']) # Evaluate using last N fitness scores
mutations = Mutations(algo=INIT_HP['ALGO'], # Algorithm
no_mutation=MUTATION_PARAMS['NO_MUT'], # No mutation
architecture=MUTATION_PARAMS['ARCH_MUT'], # Architecture mutation
new_layer_prob=MUTATION_PARAMS['NEW_LAYER'], # New layer mutation
parameters=MUTATION_PARAMS['PARAMS_MUT'], # Network parameters mutation
activation=MUTATION_PARAMS['ACT_MUT'], # Activation layer mutation
rl_hp=MUTATION_PARAMS['RL_HP_MUT'], # Learning HP mutation
rl_hp_selection=MUTATION_PARAMS['RL_HP_SELECTION'], # Learning HPs to choose from
mutation_sd=MUTATION_PARAMS['MUT_SD'], # Mutation strength
arch=NET_CONFIG['arch'], # Network architecture
rand_seed=MUTATION_PARAMS['RAND_SEED'], # Random seed
device=device)
The easiest training loop implementation is to use our training.train.train() function. It requires the agent have functions getAction() and learn().
from agilerl.training.train import train
trained_pop, pop_fitnesses = train(env=env, # Gym-style environment
env_name=INIT_HP['ENV_NAME'], # Environment name
algo=INIT_HP['ALGO'], # Algorithm
pop=agent_pop, # Population of agents
memory=memory, # Replay buffer
swap_channels=INIT_HP['CHANNELS_LAST'], # Swap image channel from last to first
n_episodes=INIT_HP['EPISODES'], # Max number of training episodes
evo_epochs=INIT_HP['EVO_EPOCHS'], # Evolution frequency
evo_loop=1, # Number of evaluation episodes per agent
target=INIT_HP['TARGET_SCORE'], # Target score for early stopping
tournament=tournament, # Tournament selection object
mutation=mutations, # Mutations object
wb=INIT_HP['WANDB']) # Weights and Biases tracking
Custom Off-policy Training Loop
Alternatively, use a custom training loop. Combining all of the above:
from agilerl.utils.utils import makeVectEnvs, initialPopulation
from agilerl.components.replay_buffer import ReplayBuffer
from agilerl.hpo.tournament import TournamentSelection
from agilerl.hpo.mutation import Mutations
import gymnasium as gym
import numpy as np
import torch
NET_CONFIG = {
'arch': 'mlp', # Network architecture
'h_size': [32, 32], # Actor hidden size
}
INIT_HP = {
'DOUBLE': True, # Use double Q-learning
'BATCH_SIZE': 128, # Batch size
'LR': 1e-3, # Learning rate
'GAMMA': 0.99, # Discount factor
'LEARN_STEP': 1, # Learning frequency
'TAU': 1e-3, # For soft update of target network parameters
'CHANNELS_LAST': False # Swap image channels dimension from last to first [H, W, C] -> [C, H, W]
}
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
env = makeVectEnvs('LunarLander-v2', num_envs=16) # Create environment
try:
state_dim = env.single_observation_space.n # Discrete observation space
one_hot = True # Requires one-hot encoding
except Exception:
state_dim = env.single_observation_space.shape # Continuous observation space
one_hot = False # Does not require one-hot encoding
try:
action_dim = env.single_action_space.n # Discrete action space
except Exception:
action_dim = env.single_action_space.shape[0] # Continuous action space
if INIT_HP['CHANNELS_LAST']:
state_dim = (state_dim[2], state_dim[0], state_dim[1])
pop = initialPopulation(algo='DQN', # Algorithm
state_dim=state_dim, # State dimension
action_dim=action_dim, # Action dimension
one_hot=one_hot, # One-hot encoding
net_config=NET_CONFIG, # Network configuration
INIT_HP=INIT_HP, # Initial hyperparameters
population_size=6, # Population size
device=device)
field_names = ["state", "action", "reward", "next_state", "done"]
memory = ReplayBuffer(action_dim=action_dim, # Number of agent actions
memory_size=10000, # Max replay buffer size
field_names=field_names, # Field names to store in memory
device=device)
tournament = TournamentSelection(tournament_size=2, # Tournament selection size
elitism=True, # Elitism in tournament selection
population_size=6, # Population size
evo_step=1) # Evaluate using last N fitness scores
mutations = Mutations(algo='DQN', # Algorithm
no_mutation=0.4, # No mutation
architecture=0.2, # Architecture mutation
new_layer_prob=0.2, # New layer mutation
parameters=0.2, # Network parameters mutation
activation=0, # Activation layer mutation
rl_hp=0.2, # Learning HP mutation
rl_hp_selection=['lr', 'batch_size'], # Learning HPs to choose from
mutation_sd=0.1, # Mutation strength
arch=NET_CONFIG['arch'], # Network architecture
rand_seed=1, # Random seed
device=device)
max_episodes = 1000 # Max training episodes
max_steps = 500 # Max steps per episode
# Exploration params
eps_start = 1.0 # Max exploration
eps_end = 0.1 # Min exploration
eps_decay = 0.995 # Decay per episode
epsilon = eps_start
evo_epochs = 5 # Evolution frequency
evo_loop = 1 # Number of evaluation episodes
# TRAINING LOOP
for idx_epi in range(max_episodes):
for agent in pop: # Loop through population
state = env.reset()[0] # Reset environment at start of episode
score = 0
for idx_step in range(max_steps):
if INIT_HP['CHANNELS_LAST']:
state = np.moveaxis(state, [3], [1])
action = agent.getAction(state, epsilon) # Get next action from agent
next_state, reward, done, _, _ = env.step(action) # Act in environment
# Save experience to replay buffer
if INIT_HP['CHANNELS_LAST']:
memory.save2memoryVectEnvs(
state, action, reward, np.moveaxis(next_state, [3], [1]), done)
else:
memory.save2memoryVectEnvs(
state, action, reward, next_state, done)
# Learn according to learning frequency
if memory.counter % agent.learn_step == 0 and len(memory) >= agent.batch_size:
experiences = memory.sample(agent.batch_size) # Sample replay buffer
agent.learn(experiences) # Learn according to agent's RL algorithm
state = next_state
score += reward
epsilon = max(eps_end, epsilon*eps_decay) # Update epsilon for exploration
# Now evolve population if necessary
if (idx_epi+1) % evo_epochs == 0:
# Evaluate population
fitnesses = [agent.test(env, swap_channels=INIT_HP['CHANNELS_LAST'], max_steps=max_steps, loop=evo_loop) for agent in pop]
print(f'Episode {idx_epi+1}/{max_episodes}')
print(f'Fitnesses: {["%.2f"%fitness for fitness in fitnesses]}')
print(f'100 fitness avgs: {["%.2f"%np.mean(agent.fitness[-100:]) for agent in pop]}')
# Tournament selection and population mutation
elite, pop = tournament.select(pop)
pop = mutations.mutation(pop)
env.close()
On-policy reinforcement learning
While off-policy RL algorithms can be considered more efficient than on-policy algorithms, due to their ability to learn from experiences collected using a different or previous policy, we have still chosen to include an efficient, evolvable PPO implementation in AgileRL. This algorithm can be used in a variety of settings, with both discrete and continuous actions, and is widely popular across domains including robotics, games, finance, and RLHF.
The setup for PPO is very similar to the off-policy example above, except it does not require the use of an experience replay buffer. It also requires some different hyperparameters, shown below in the custom loop.
The easiest way to train a population of agents using PPO is to use our online training function:
from agilerl.training.train_on_policy import train
trained_pop, pop_fitnesses = train(env=env, # Gym-style environment
env_name=INIT_HP['ENV_NAME'], # Environment name
algo=INIT_HP['ALGO'], # Algorithm
pop=agent_pop, # Population of agents
swap_channels=INIT_HP['CHANNELS_LAST'], # Swap image channel from last to first
n_episodes=INIT_HP['EPISODES'], # Max number of training episodes
evo_epochs=INIT_HP['EVO_EPOCHS'], # Evolution frequency
evo_loop=1, # Number of evaluation episodes per agent
target=INIT_HP['TARGET_SCORE'], # Target score for early stopping
tournament=tournament, # Tournament selection object
mutation=mutations, # Mutations object
wb=INIT_HP['WANDB']) # Weights and Biases tracking
Custom On-policy Training Loop
Alternatively, use a custom training loop:
import numpy as np
import torch
from tqdm import trange
from agilerl.hpo.mutation import Mutations
from agilerl.hpo.tournament import TournamentSelection
from agilerl.utils.utils import initialPopulation, makeVectEnvs
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
NET_CONFIG = {
"arch": "mlp", # Network architecture
"h_size": [32, 32], # Actor hidden size
}
INIT_HP = {
"POPULATION_SIZE": 6, # Population size
"DISCRETE_ACTIONS": True, # Discrete action space
"BATCH_SIZE": 128, # Batch size
"LR": 1e-3, # Learning rate
"GAMMA": 0.99, # Discount factor
"GAE_LAMBDA": 0.95, # Lambda for general advantage estimation
"ACTION_STD_INIT": 0.6, # Initial action standard deviation
"CLIP_COEF": 0.2, # Surrogate clipping coefficient
"ENT_COEF": 0.01, # Entropy coefficient
"VF_COEF": 0.5, # Value function coefficient
"MAX_GRAD_NORM": 0.5, # Maximum norm for gradient clipping
"TARGET_KL": None, # Target KL divergence threshold
"UPDATE_EPOCHS": 4, # Number of policy update epochs
# Swap image channels dimension from last to first [H, W, C] -> [C, H, W]
"CHANNELS_LAST": False,
}
env = makeVectEnvs("LunarLander-v2", num_envs=8) # Create environment
try:
state_dim = env.single_observation_space.n # Discrete observation space
one_hot = True # Requires one-hot encoding
except Exception:
state_dim = env.single_observation_space.shape # Continuous observation space
one_hot = False # Does not require one-hot encoding
try:
action_dim = env.single_action_space.n # Discrete action space
except Exception:
action_dim = env.single_action_space.shape[0] # Continuous action space
if INIT_HP["CHANNELS_LAST"]:
state_dim = (state_dim[2], state_dim[0], state_dim[1])
pop = initialPopulation(
algo="PPO", # Algorithm
state_dim=state_dim, # State dimension
action_dim=action_dim, # Action dimension
one_hot=one_hot, # One-hot encoding
net_config=NET_CONFIG, # Network configuration
INIT_HP=INIT_HP, # Initial hyperparameters
population_size=INIT_HP["POPULATION_SIZE"], # Population size
device=device,
)
tournament = TournamentSelection(
tournament_size=2, # Tournament selection size
elitism=True, # Elitism in tournament selection
population_size=INIT_HP["POPULATION_SIZE"], # Population size
evo_step=1,
) # Evaluate using last N fitness scores
mutations = Mutations(
algo="PPO", # Algorithm
no_mutation=0.4, # No mutation
architecture=0.2, # Architecture mutation
new_layer_prob=0.2, # New layer mutation
parameters=0.2, # Network parameters mutation
activation=0, # Activation layer mutation
rl_hp=0.2, # Learning HP mutation
rl_hp_selection=["lr", "batch_size"], # Learning HPs to choose from
mutation_sd=0.1, # Mutation strength
arch=NET_CONFIG["arch"], # Network architecture
rand_seed=1, # Random seed
device=device,
)
max_episodes = 1000 # Max training episodes
max_steps = 500 # Max steps per episode
evo_epochs = 5 # Evolution frequency
evo_loop = 3 # Number of evaluation episodes
print("Training...")
# TRAINING LOOP
for idx_epi in trange(max_episodes):
for agent in pop: # Loop through population
state = env.reset()[0] # Reset environment at start of episode
score = 0
states = []
actions = []
log_probs = []
rewards = []
dones = []
values = []
for idx_step in range(max_steps):
if INIT_HP["CHANNELS_LAST"]:
state = np.moveaxis(state, [3], [1])
# Get next action from agent
action, log_prob, _, value = agent.getAction(state)
next_state, reward, done, trunc, _ = env.step(
action
) # Act in environment
states.append(state)
actions.append(action)
log_probs.append(log_prob)
rewards.append(reward)
dones.append(done)
values.append(value)
state = next_state
score += reward
agent.scores.append(score)
experiences = (
states,
actions,
log_probs,
rewards,
dones,
values,
next_state,
)
# Learn according to agent's RL algorithm
agent.learn(experiences)
agent.steps[-1] += idx_step + 1
# Now evolve population if necessary
if (idx_epi + 1) % evo_epochs == 0:
# Evaluate population
fitnesses = [
agent.test(
env,
swap_channels=INIT_HP["CHANNELS_LAST"],
max_steps=max_steps,
loop=evo_loop,
)
for agent in pop
]
print(f"Episode {idx_epi+1}/{max_episodes}")
print(f'Fitnesses: {["%.2f"%fitness for fitness in fitnesses]}')
print(
f'100 fitness avgs: {["%.2f"%np.mean(agent.fitness[-100:]) for agent in pop]}'
)
# Tournament selection and population mutation
elite, pop = tournament.select(pop)
pop = mutations.mutation(pop)
env.close()
Train an agent on data (Offline)
Like with online RL, above, there are some meta-hyperparameters and settings that must be set before starting training. These are defined in INIT_HP, for general parameters, and MUTATION_PARAMS, which define the evolutionary probabilities, and NET_CONFIG, which defines the network architecture. For example:
INIT_HP = {
'ENV_NAME': 'CartPole-v1', # Gym environment name
'DATASET': 'data/cartpole/cartpole_random_v1.1.0.h5', # Offline RL dataset
'ALGO': 'CQN', # Algorithm
'DOUBLE': True, # Use double Q-learning
# Swap image channels dimension from last to first [H, W, C] -> [C, H, W]
'CHANNELS_LAST': False,
'BATCH_SIZE': 256, # Batch size
'LR': 1e-3, # Learning rate
'EPISODES': 2000, # Max no. episodes
'TARGET_SCORE': 200., # Early training stop at avg score of last 100 episodes
'GAMMA': 0.99, # Discount factor
'MEMORY_SIZE': 10000, # Max memory buffer size
'LEARN_STEP': 1, # Learning frequency
'TAU': 1e-3, # For soft update of target parameters
'TOURN_SIZE': 2, # Tournament size
'ELITISM': True, # Elitism in tournament selection
'POP_SIZE': 6, # Population size
'EVO_EPOCHS': 20, # Evolution frequency
'POLICY_FREQ': 2, # Policy network update frequency
'WANDB': True # Log with Weights and Biases
}
MUTATION_PARAMS = {
# Relative probabilities
'NO_MUT': 0.4, # No mutation
'ARCH_MUT': 0.2, # Architecture mutation
'NEW_LAYER': 0.2, # New layer mutation
'PARAMS_MUT': 0.2, # Network parameters mutation
'ACT_MUT': 0, # Activation layer mutation
'RL_HP_MUT': 0.2, # Learning HP mutation
'RL_HP_SELECTION': ['lr', 'batch_size'], # Learning HPs to choose from
'MUT_SD': 0.1, # Mutation strength
'RAND_SEED': 1, # Random seed
}
NET_CONFIG = {
'arch': 'mlp', # Network architecture
'h_size': [32, 32], # Actor hidden size
}
First, use utils.utils.initialPopulation to create a list of agents - our population that will evolve and mutate to the optimal hyperparameters.
from agilerl.utils.utils import makeVectsEnvs, initialPopulation
import torch
import h5py
import gymnasium as gym
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
env = makeVectEnvs(INIT_HP['ENV_NAME'], num_envs=1)
try:
state_dim = env.single_observation_space.n # Discrete observation space
one_hot = True # Requires one-hot encoding
except Exception:
state_dim = env.single_observation_space.shape # Continuous observation space
one_hot = False # Does not require one-hot encoding
try:
action_dim = env.single_action_space.n # Discrete action space
except Exception:
action_dim = env.single_action_space.shape[0] # Continuous action space
if INIT_HP['CHANNELS_LAST']:
state_dim = (state_dim[2], state_dim[0], state_dim[1])
dataset = h5py.File(INIT_HP['DATASET'], 'r')
agent_pop = initialPopulation(algo=INIT_HP['ALGO'], # Algorithm
state_dim=state_dim, # State dimension
action_dim=action_dim, # Action dimension
one_hot=one_hot, # One-hot encoding
net_config=NET_CONFIG, # Network configuration
INIT_HP=INIT_HP, # Initial hyperparameters
population_size=INIT_HP['POP_SIZE'], # Population size
device=device)
Next, create the tournament, mutations and experience replay buffer objects that allow agents to share memory and efficiently perform evolutionary HPO.
from agilerl.components.replay_buffer import ReplayBuffer
from agilerl.hpo.tournament import TournamentSelection
from agilerl.hpo.mutation import Mutations
import torch
field_names = ["state", "action", "reward", "next_state", "done"]
memory = ReplayBuffer(action_dim=action_dim, # Number of agent actions
memory_size=INIT_HP['MEMORY_SIZE'], # Max replay buffer size
field_names=field_names, # Field names to store in memory
device=device)
tournament = TournamentSelection(tournament_size=INIT_HP['TOURN_SIZE'], # Tournament selection size
elitism=INIT_HP['ELITISM'], # Elitism in tournament selection
population_size=INIT_HP['POP_SIZE'], # Population size
evo_step=INIT_HP['EVO_EPOCHS']) # Evaluate using last N fitness scores
mutations = Mutations(algo=INIT_HP['ALGO'], # Algorithm
no_mutation=MUTATION_PARAMS['NO_MUT'], # No mutation
architecture=MUTATION_PARAMS['ARCH_MUT'], # Architecture mutation
new_layer_prob=MUTATION_PARAMS['NEW_LAYER'], # New layer mutation
parameters=MUTATION_PARAMS['PARAMS_MUT'], # Network parameters mutation
activation=MUTATION_PARAMS['ACT_MUT'], # Activation layer mutation
rl_hp=MUTATION_PARAMS['RL_HP_MUT'], # Learning HP mutation
rl_hp_selection=MUTATION_PARAMS['RL_HP_SELECTION'], # Learning HPs to choose from
mutation_sd=MUTATION_PARAMS['MUT_SD'], # Mutation strength
arch=NET_CONFIG['arch'], # Network architecture
rand_seed=MUTATION_PARAMS['RAND_SEED'], # Random seed
device=device)
The easiest training loop implementation is to use our training.train_offline.train() function. It requires the agent have functions getAction() and learn().
from agilerl.training.train_offline import train
trained_pop, pop_fitnesses = train(env=env, # Gym-style environment
env_name=INIT_HP['ENV_NAME'], # Environment name
dataset=dataset, # Offline dataset
algo=INIT_HP['ALGO'], # Algorithm
pop=agent_pop, # Population of agents
memory=memory, # Replay buffer
swap_channels=INIT_HP['CHANNELS_LAST'], # Swap image channel from last to first
n_episodes=INIT_HP['EPISODES'], # Max number of training episodes
evo_epochs=INIT_HP['EVO_EPOCHS'], # Evolution frequency
evo_loop=1, # Number of evaluation episodes per agent
target=INIT_HP['TARGET_SCORE'], # Target score for early stopping
tournament=tournament, # Tournament selection object
mutation=mutations, # Mutations object
wb=INIT_HP['WANDB']) # Weights and Biases tracking
Custom Offline Training Loop
Alternatively, use a custom training loop. Combining all of the above:
from agilerl.utils.utils import makeVectEnvs, initialPopulation
from agilerl.components.replay_buffer import ReplayBuffer
from agilerl.hpo.tournament import TournamentSelection
from agilerl.hpo.mutation import Mutations
import h5py
import numpy as np
import torch
from tqdm import trange
NET_CONFIG = {
'arch': 'mlp', # Network architecture
'h_size': [32, 32], # Actor hidden size
}
INIT_HP = {
'DOUBLE': True, # Use double Q-learning
'BATCH_SIZE': 128, # Batch size
'LR': 1e-3, # Learning rate
'GAMMA': 0.99, # Discount factor
'LEARN_STEP': 1, # Learning frequency
'TAU': 1e-3, # For soft update of target network parameters
'CHANNELS_LAST': False # Swap image channels dimension from last to first [H, W, C] -> [C, H, W]
}
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
env = gym.make('CartPole-v1') # Create environment
dataset = h5py.File('data/cartpole/cartpole_random_v1.1.0.h5', 'r') # Load dataset
try:
state_dim = env.single_observation_space.n # Discrete observation space
one_hot = True # Requires one-hot encoding
except Exception:
state_dim = env.single_observation_space.shape # Continuous observation space
one_hot = False # Does not require one-hot encoding
try:
action_dim = env.single_action_space.n # Discrete action space
except Exception:
action_dim = env.single_action_space.shape[0] # Continuous action space
if INIT_HP['CHANNELS_LAST']:
state_dim = (state_dim[2], state_dim[0], state_dim[1])
pop = initialPopulation(algo='CQN', # Algorithm
state_dim=state_dim, # State dimension
action_dim=action_dim, # Action dimension
one_hot=one_hot, # One-hot encoding
net_config=NET_CONFIG, # Network configuration
INIT_HP=INIT_HP, # Initial hyperparameters
population_size=6, # Population size
device=device)
field_names = ["state", "action", "reward", "next_state", "done"]
memory = ReplayBuffer(action_dim=action_dim, # Number of agent actions
memory_size=10000, # Max replay buffer size
field_names=field_names, # Field names to store in memory
device=device)
tournament = TournamentSelection(tournament_size=2, # Tournament selection size
elitism=True, # Elitism in tournament selection
population_size=6, # Population size
evo_step=1) # Evaluate using last N fitness scores
mutations = Mutations(algo='CQN', # Algorithm
no_mutation=0.4, # No mutation
architecture=0.2, # Architecture mutation
new_layer_prob=0.2, # New layer mutation
parameters=0.2, # Network parameters mutation
activation=0, # Activation layer mutation
rl_hp=0.2, # Learning HP mutation
rl_hp_selection=['lr', 'batch_size'], # Learning HPs to choose from
mutation_sd=0.1, # Mutation strength
arch=NET_CONFIG['arch'], # Network architecture
rand_seed=1, # Random seed
device=device)
max_episodes = 1000 # Max training episodes
max_steps = 500 # Max steps per episode
evo_epochs = 5 # Evolution frequency
evo_loop = 1 # Number of evaluation episodes
# Save transitions to replay buffer
dataset_length = dataset['rewards'].shape[0]
for i in trange(dataset_length-1):
state = dataset['observations'][i]
next_state = dataset['observations'][i+1]
if INIT_HP['CHANNELS_LAST']:
state = np.moveaxis(state, [3], [1])
next_state = np.moveaxis(next_state, [3], [1])
action = dataset['actions'][i]
reward = dataset['rewards'][i]
done = bool(dataset['terminals'][i])
# Save experience to replay buffer
memory.save2memory(state, action, reward, next_state, done)
# TRAINING LOOP
for idx_epi in trange(max_episodes):
for agent in pop: # Loop through population
for idx_step in range(max_steps):
experiences = memory.sample(agent.batch_size) # Sample replay buffer
# Learn according to agent's RL algorithm
agent.learn(experiences)
# Now evolve population if necessary
if (idx_epi+1) % evo_epochs == 0:
# Evaluate population
fitnesses = [agent.test(env, swap_channels=False, max_steps=max_steps, loop=evo_loop) for agent in pop]
print(f'Episode {idx_epi+1}/{max_episodes}')
print(f'Fitnesses: {["%.2f"%fitness for fitness in fitnesses]}')
print(f'100 fitness avgs: {["%.2f"%np.mean(agent.fitness[-100:]) for agent in pop]}')
# Tournament selection and population mutation
elite, pop = tournament.select(pop)
pop = mutations.mutation(pop)
env.close()
Train an agent on a language environment (RLHF)
We implement RLHF on Wordle, and use ILQL to finetune our model. To create your own language environment,
see https://github.com/Sea-Snell/Implicit-Language-Q-Learning.
The EvolvableGPT class allows us to combine LLMs and transformer architectures with evolvable HPO, which can massively reduce the time taken to finetune
these expensive models. Due to the vast number of parameters and settings involved in training a Large Language Model (LLM) on human feedback, these are defined in
configs.
In order to finetune a model with RLHF, we need a trained model as a starting point. We can use behavioural cloning (BC, supervised learning) to build this first version of the model. To train your own model from scratch:
python run_bc_lm.py
If you want to use pretrained model weights, these can be defined in configs/wordle/train_bc.yaml in model: load:.
Similarly, to then run ILQL and perform RLHF on the BC model:
python run_ilql.py
Distributed training
AgileRL can also be used for distributed training if you have multiple devices you want to take advantage of. We use the HuggingFace Accelerate library to implement this in an open manner, without hiding behind too many layers of abstraction. This should make implementations simple, but also highly customisable, by continuing to expose the PyTorch training loop beneath it all.
To launch distributed training scripts in bash, use accelerate launch. To customise the distributed training properties, specify the key --config_file. An example
config file has been provided at configs/accelerate/accelerate.yaml.
Putting this all together, launching a distributed training script can be done as follows:
accelerate_launch --config_file configs/accelerate/accelerate.yaml demo_online_distributed.py
There are some key considerations to bear in mind when implementing a distributed training run:
- If you only want to execute something once, rather than repeating it for each process, e.g printing a statement, logging to W&B, then use
if accelerator.is_main_process:. - Training happens in parallel on each device, meaning that steps in a RL environment happen on each device too. In order to count the number of global training steps taken, you must multiply the number of steps you have taken on a singular device by the number of devices (assuming they are equal). If you want to use distributed training to train more quickly, and normally you would train for 100,000 steps on one device, you can now train for just 25,000 steps if using four devices.
Example distributed training loop:
from agilerl.utils.utils import makeVectEnvs, initialPopulation
from agilerl.components.replay_buffer import ReplayBuffer
from agilerl.components.replay_data import ReplayDataset
from agilerl.components.sampler import Sampler
from agilerl.hpo.tournament import TournamentSelection
from agilerl.hpo.mutation import Mutations
from accelerate import Accelerator
import numpy as np
import os
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from tqdm import trange
if __name__ == '__main__':
accelerator = Accelerator()
NET_CONFIG = {
'arch': 'mlp', # Network architecture
'h_size': [32, 32], # Actor hidden size
}
INIT_HP = {
'POPULATION_SIZE': 4, # Population size
'DOUBLE': True, # Use double Q-learning in DQN or CQN
'BATCH_SIZE': 128, # Batch size
'LR': 1e-3, # Learning rate
'GAMMA': 0.99, # Discount factor
'LEARN_STEP': 1, # Learning frequency
'TAU': 1e-3, # For soft update of target network parameters
'POLICY_FREQ': 2, # DDPG target network update frequency vs policy network
# Swap image channels dimension from last to first [H, W, C] -> [C, H, W]
'CHANNELS_LAST': False
}
env = makeVectEnvs('LunarLander-v2', num_envs=8) # Create environment
try:
state_dim = env.single_observation_space.n # Discrete observation space
one_hot = True # Requires one-hot encoding
except Exception:
state_dim = env.single_observation_space.shape # Continuous observation space
one_hot = False # Does not require one-hot encoding
try:
action_dim = env.single_action_space.n # Discrete action space
except Exception:
action_dim = env.single_action_space.shape[0] # Continuous action space
if INIT_HP['CHANNELS_LAST']:
state_dim = (state_dim[2], state_dim[0], state_dim[1])
pop = initialPopulation(algo='DQN', # Algorithm
state_dim=state_dim, # State dimension
action_dim=action_dim, # Action dimension
one_hot=one_hot, # One-hot encoding
net_config=NET_CONFIG, # Network configuration
INIT_HP=INIT_HP, # Initial hyperparameters
population_size=INIT_HP['POPULATION_SIZE'], # Population size
accelerator=accelerator) # Accelerator
field_names = ["state", "action", "reward", "next_state", "done"]
memory = ReplayBuffer(action_dim=action_dim, # Number of agent actions
memory_size=10000, # Max replay buffer size
field_names=field_names) # Field names to store in memory
replay_dataset = ReplayDataset(memory, INIT_HP['BATCH_SIZE'])
replay_dataloader = DataLoader(replay_dataset, batch_size=None)
replay_dataloader = accelerator.prepare(replay_dataloader)
sampler = Sampler(distributed=True,
dataset=replay_dataset,
dataloader=replay_dataloader)
tournament = TournamentSelection(tournament_size=2, # Tournament selection size
elitism=True, # Elitism in tournament selection
population_size=INIT_HP['POPULATION_SIZE'], # Population size
evo_step=1) # Evaluate using last N fitness scores
mutations = Mutations(algo='DQN', # Algorithm
no_mutation=0.4, # No mutation
architecture=0.2, # Architecture mutation
new_layer_prob=0.2, # New layer mutation
parameters=0.2, # Network parameters mutation
activation=0, # Activation layer mutation
rl_hp=0.2, # Learning HP mutation
rl_hp_selection=['lr', 'batch_size'], # Learning HPs to choose from
mutation_sd=0.1, # Mutation strength
arch=NET_CONFIG['arch'], # Network architecture
rand_seed=1, # Random seed
accelerator=accelerator) # Accelerator)
max_episodes = 1000 # Max training episodes
max_steps = 500 # Max steps per episode
# Exploration params
eps_start = 1.0 # Max exploration
eps_end = 0.1 # Min exploration
eps_decay = 0.995 # Decay per episode
epsilon = eps_start
evo_epochs = 5 # Evolution frequency
evo_loop = 1 # Number of evaluation episodes
accel_temp_models_path = 'models/{}'.format('LunarLander-v2')
if accelerator.is_main_process:
if not os.path.exists(accel_temp_models_path):
os.makedirs(accel_temp_models_path)
print(f'\nDistributed training on {accelerator.device}...')
# TRAINING LOOP
for idx_epi in trange(max_episodes):
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
for agent in pop: # Loop through population
state = env.reset()[0] # Reset environment at start of episode
score = 0
for idx_step in range(max_steps):
# Get next action from agent
action = agent.getAction(state, epsilon)
next_state, reward, done, _, _ = env.step(
action) # Act in environment
# Save experience to replay buffer
memory.save2memoryVectEnvs(
state, action, reward, next_state, done)
# Learn according to learning frequency
if memory.counter % agent.learn_step == 0 and len(
memory) >= agent.batch_size:
# Sample dataloader
experiences = sampler.sample(agent.batch_size)
# Learn according to agent's RL algorithm
agent.learn(experiences)
state = next_state
score += reward
# Update epsilon for exploration
epsilon = max(eps_end, epsilon * eps_decay)
# Now evolve population if necessary
if (idx_epi + 1) % evo_epochs == 0:
# Evaluate population
fitnesses = [
agent.test(
env,
swap_channels=False,
max_steps=max_steps,
loop=evo_loop) for agent in pop]
if accelerator.is_main_process:
print(f'Episode {idx_epi+1}/{max_episodes}')
print(f'Fitnesses: {["%.2f"%fitness for fitness in fitnesses]}')
print(f'100 fitness avgs: {["%.2f"%np.mean(agent.fitness[-100:]) for agent in pop]}')
# Tournament selection and population mutation
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
for model in pop:
model.unwrap_models()
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
if accelerator.is_main_process:
elite, pop = tournament.select(pop)
pop = mutations.mutation(pop)
for pop_i, model in enumerate(pop):
model.saveCheckpoint(f'{accel_temp_models_path}/DQN_{pop_i}.pt')
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
if not accelerator.is_main_process:
for pop_i, model in enumerate(pop):
model.loadCheckpoint(f'{accel_temp_models_path}/DQN_{pop_i}.pt')
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
for model in pop:
model.wrap_models()
env.close()
Multi-agent training
As in previous examples, before starting training, meta-hyperparameters INIT_HP, MUTATION_PARAMS, and NET_CONFIG must first be defined.
NET_CONFIG = {
'arch': 'mlp', # Network architecture
'h_size': [32, 32], # Actor hidden size
}
INIT_HP = {
'ALGO': 'MADDPG', # Algorithm
'BATCH_SIZE': 512, # Batch size
'LR': 0.01, # Learning rate
'EPISODES': 10_000, # Max no. episodes
'GAMMA': 0.95, # Discount factor
'MEMORY_SIZE': 1_000_000, # Max memory buffer size
'LEARN_STEP': 5, # Learning frequency
'TAU': 0.01, # For soft update of target parameters
# Swap image channels dimension from last to first [H, W, C] -> [C, H, W]
'CHANNELS_LAST': False,
"WANDB": False # Start run with Weights&Biases
}
MUTATION_PARAMS = {
"NO_MUT": 0.4, # No mutation
"ARCH_MUT": 0.2, # Architecture mutation
"NEW_LAYER": 0.2, # New layer mutation
"PARAMS_MUT": 0.2, # Network parameters mutation
"ACT_MUT": 0, # Activation layer mutation
"RL_HP_MUT": 0.2, # Learning HP mutation
# Learning HPs to choose from
"RL_HP_SELECTION": ["lr", "batch_size", "learn_step"],
"MUT_SD": 0.1, # Mutation strength
"RAND_SEED": 42, # Random seed
"MIN_LR": 0.0001, # Define max and min limits for mutating RL hyperparams
"MAX_LR": 0.01,
"MIN_LEARN_STEP": 1,
"MAX_LEARN_STEP": 200,
"MIN_BATCH_SIZE": 8,
"MAX_BATCH_SIZE": 1024
}
Use utils.utils.initialPopulation to create a list of agents - our population that will evolve and mutate to the optimal hyperparameters.
from agilerl.utils.utils import initialPopulation
from pettingzoo.mpe import simple_speaker_listener_v4
import torch
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
env = simple_speaker_listener_v4.parallel_env(continuous_actions=True)
env.reset()
# Configure the multi-agent algo input arguments
try:
state_dim = [env.observation_space(agent).n for agent in env.agents]
one_hot = True
except Exception:
state_dim = [env.observation_space(agent).shape for agent in env.agents]
one_hot = False
try:
action_dim = [env.action_space(agent).n for agent in env.agents]
INIT_HP['DISCRETE_ACTIONS'] = True
INIT_HP['MAX_ACTION'] = None
INIT_HP['MIN_ACTION'] = None
except Exception:
action_dim = [env.action_space(agent).shape[0] for agent in env.agents]
INIT_HP['DISCRETE_ACTIONS'] = False
INIT_HP['MAX_ACTION'] = [env.action_space(agent).high for agent in env.agents]
INIT_HP['MIN_ACTION'] = [env.action_space(agent).low for agent in env.agents]
if INIT_HP['CHANNELS_LAST']:
state_dim = [(state_dim[2], state_dim[0], state_dim[1]) for state_dim in state_dim]
INIT_HP['N_AGENTS'] = env.num_agents
INIT_HP['AGENT_IDS'] = [agent_id for agent_id in env.agents]
agent_pop = initialPopulation(algo=INIT_HP['ALGO'],
state_dim=state_dim,
action_dim=action_dim,
one_hot=one_hot,
net_config=NET_CONFIG,
INIT_HP=INIT_HP,
population_size=6,
device=device)
Next, create the tournament, mutations and experience replay buffer objects that allow agents to share memory and efficiently perform evolutionary HPO.
from agilerl.components.multi_agent_replay_buffer import MultiAgentReplayBuffer
from agilerl.hpo.tournament import TournamentSelection
from agilerl.hpo.mutation import Mutations
field_names = ["state", "action", "reward", "next_state", "done"]
memory = MultiAgentReplayBuffer(memory_size=1_000_000, # Max replay buffer size
field_names=field_names, # Field names to store in memory
agent_ids=INIT_HP['AGENT_IDS'],
device=torch.device("cuda"))
tournament = TournamentSelection(tournament_size=2, # Tournament selection size
elitism=True, # Elitism in tournament selection
population_size=6, # Population size
evo_step=1) # Evaluate using last N fitness scores
mutations = Mutations(algo=INIT_HP['ALGO'],
no_mutation=MUTATION_PARAMS['NO_MUT'],
architecture=MUTATION_PARAMS['ARCH_MUT'],
new_layer_prob=MUTATION_PARAMS['NEW_LAYER'],
parameters=MUTATION_PARAMS['PARAMS_MUT'],
activation=MUTATION_PARAMS['ACT_MUT'],
rl_hp=MUTATION_PARAMS['RL_HP_MUT'],
rl_hp_selection=MUTATION_PARAMS['RL_HP_SELECTION'],
mutation_sd=MUTATION_PARAMS['MUT_SD'],
min_lr=MUTATION_PARAMS['MIN_LR'],
max_lr=MUTATION_PARAMS['MAX_LR'],
min_learn_step=MUTATION_PARAMS['MIN_LEARN_STEP'],
max_learn_step=MUTATION_PARAMS['MAX_LEARN_STEP'],
min_batch_size=MUTATION_PARAMS['MIN_BATCH_SIZE'],
max_batch_size=MUTATION_PARAMS['MAX_BATCH_SIZE'],
agent_ids=INIT_HP['AGENT_IDS'],
arch=NET_CONFIG['arch'],
rand_seed=MUTATION_PARAMS['RAND_SEED'],
device=device)
The easiest training loop implementation is to use our training.train_multi_agent.train_multi_agent() function. It requires the agent have functions getAction() and learn().
from agilerl.training.train_multi_agent import train_multi_agent
import torch
trained_pop, pop_fitnesses = train_multi_agent(env=env, # Pettingzoo-style environment
env_name='simple_speaker_listener_v4', # Environment name
algo=INIT_HP['ALGO'], # Algorithm
pop=agent_pop, # Population of agents
memory=memory, # Replay buffer
INIT_HP=INIT_HP, # IINIT_HP dictionary
MUT_P=MUTATION_PARAMS, # MUTATION_PARAMS dictionary
net_config=NET_CONFIG, # Network configuration
swap_channels=INIT_HP['CHANNELS_LAST'], # Swap image channel from last to first
n_episodes=INIT_HP['EPISODES'], # Max number of training episodes
evo_epochs=20, # Evolution frequency
evo_loop=1, # Number of evaluation episodes per agent
max_steps=900, # Max steps to take in the environment
target=200., # Target score for early stopping
tournament=tournament, # Tournament selection object
mutation=mutations, # Mutations object
wb=INIT_HP["WANDB"]) # Weights and Biases tracking
View documentation.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.















