Compass-aligned Distributional Embeddings
Project description
Compass-aligned Distributional Embeddings



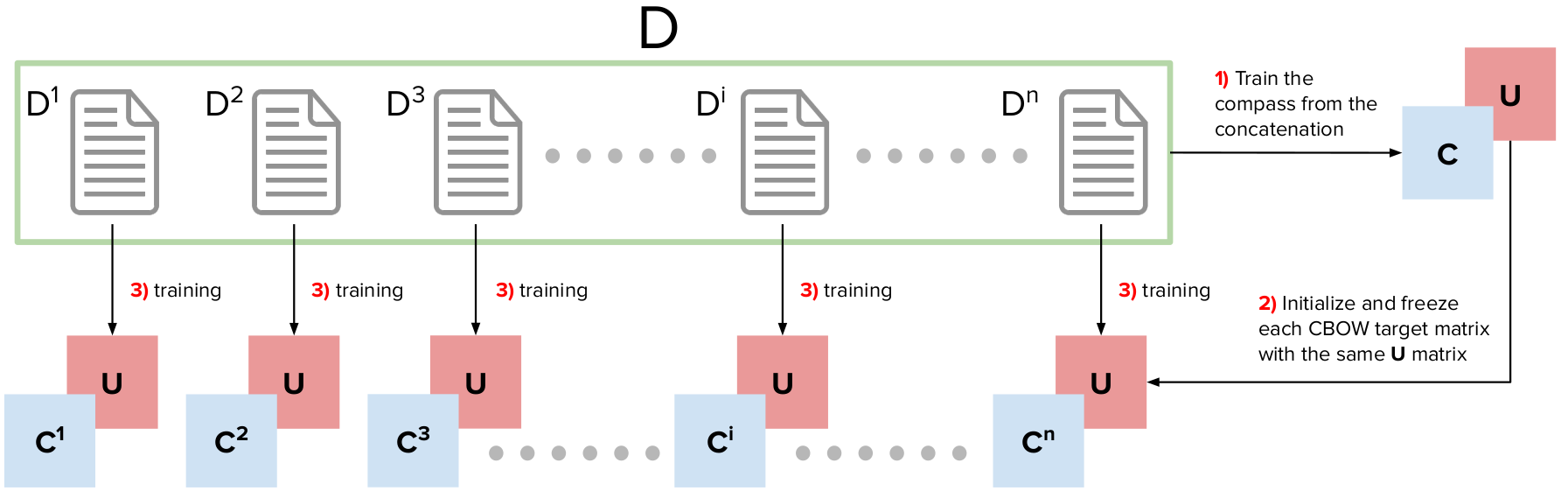
This package contains Python code to generate compass aligned distributional embeddings. Comparing word vectors in different corpora requires alignment. We propose a method to aligned distributional representation based on word2vec. This method is efficient and it is based on a simple heuristic: we train a general word embedding, the compass and we use this embedding to freeze one of the layers of the CBOW architecture.
See the AAAI and Arxiv pre-print papers for more details.
Reference
This work is based on the following papers: AAAI and Arxiv-preprint
Bianchi, F., Di Carlo, V., Nicoli, P., & Palmonari, M. (2019). Compass-aligned Distributional Embeddings for Studying Semantic Differences across Corpora. Arxiv. https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.06519
Di Carlo, V., Bianchi, F., & Palmonari, M. (2019). Training Temporal Word Embeddings with a Compass. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 33(01), 6326-6334. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33016326
Abstract
Word2vec is one of the most used algorithms to generate word embeddings because of a good mix of efficiency, quality of the generated representations and cognitive grounding. However, word meaning is not static and depends on the context in which words are used. Differences in word meaning that depends on time, location, topic, and other factors, can be studied by analyzing embeddings generated from different corpora in collections that are representative of these factors. For example, language evolution can be studied using a collection of news articles published in different time periods. In this paper, we present a general framework to support cross-corpora language studies with word embeddings, where embeddings generated from different corpora can be compared to find correspondences and differences in meaning across the corpora. CADE is the core component of our framework and solves the key problem of aligning the embeddings generated from different corpora. In particular, we focus on providing solid evidence about the effectiveness, generality, and robustness of CADE. To this end, we conduct quantitative and qualitative experiments in different domains, from temporal word embeddings to language localization and topical analysis. The results of our experiments suggest that CADE achieves state-of-the-art or superior performance on tasks where several competing approaches are available, yet providing a general method that can be used in a variety of domains. Finally, our experiments shed light on the conditions under which the alignment is reliable, which substantially depends on the degree of cross-corpora vocabulary overlap.
Note
We have modified the gensim implementation to suits our need, when you install this package remember to do it in a virtualenv or the installation is going to overwrite your own gensim module. Important: always create a virtual environment because CADE uses a custom version of the gensim library.
Installing
clone the repository
virtualenv -p python3.6 envsource env/bin/activatepip install cythonpip install git+https://github.com/valedica/gensim.gitcd in repository
pip install -e .
Jupyter: you can use this in a jupyter-notebook, but remember that you need the virtual environment! In the following the commands you need to use, but for a more detailed description of what we are doing see this link.
you need to install the virtual environment inside jupyter
source env/bin/activate(venv) $ pip install ipykernel(venv) $ ipython kernel install --user --name=cade_kernelyou will find the “cade_kernel” when you create a new notebook
Guide
Remember: when you call the training method of
CADEthe class creates a “model/” folder where it is going to save the trained objects. The compass will be trained as first element and it will be saved in that folder. If you want to overwrite it remember to set the parameteroverwrite=True, otherwise it will reload the already trained compass.What do you need: Different corpora you want to compare (i.e., text from 1991, text from 1992 / text from the New York Times, text from The Guardian … etc…) and the concatenation of those text slices (the compass).
The compass should be the concatenation of the slice you want to align. In the next code section you will see that we are going to use arxiv papers text from two different years. The “compass.txt” file contains the concatenation of both slices.
How To Use
Training
Suppose you have corpora you want to compare text “arxiv_14.txt” and “arxiv_9.txt”. First of all, create the concatenation of these two and create a “compass.txt” file. Now you can train the compass.
from cade.cade import CADE
from gensim.models.word2vec import Word2Vec
aligner = CADE(size=30, siter=10, diter=10, workers=4)
# train the compass: the text should be the concatenation of the text from the slices
aligner.train_compass("examples/training/compass.txt", overwrite=False) # keep an eye on the overwrite behaviourYou can see that the class covers the same parameters the Gensim word2vec library has. “siter” refers to the compass training iterations while “diter” refers to the training iteration of the specific slices. After this first training you can train the slices:
# now you can train slices and they will be already aligned
# these are gensim word2vec objects
slice_one = aligner.train_slice("examples/training/arxiv_14.txt", save=True)
slice_two = aligner.train_slice("examples/training/arxiv_9.txt", save=True)These two slices are now aligned and can be compared!
Load Data
You can load data has you do with gensim.
model1 = Word2Vec.load("model/arxiv_14.model")
model2 = Word2Vec.load("model/arxiv_9.model")People
Valerio Di Carlo
Matteo Palmonari (matteo.palmonari@unimib.it)
Credits
This package was created with Cookiecutter and the audreyr/cookiecutter-pypackage project template.
History
0.1.0 (2019-09-11)
First release on PyPI.
Project details
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.











