Display all Python process output character-by-character
Project description
dramatic
The dramatic module includes utilities to cause all text output to display character-by-character (it prints dramatically).
Note: This project is based on a Python Morsels exercise. If you're working on that exercise right now, please don't look at the source code for this! 😉

Usage
The dramatic module is available on PyPI.
You can install it with pip:
$ python3 -m pip install dramatic
There are four primary ways to use the utilities in the dramatic module:
- As a context manager that temporarily makes output display dramatically
- As a decorator that temporarily makes output display dramatically
- Using a
dramatic.start()function that makes output display dramatically - Using a
dramatic.printfunction to display specific text dramatically
Dramatic Context Manager
The dramatic.output context manager will temporarily cause all standard output and standard error to display dramatically:
import dramatic
def main():
print("This function prints")
with dramatic.output:
main()
To change the printing speed from the default of 75 characters per second to another value (30 characters per second in this case) use the at_speed method:
import dramatic
def main():
print("This function prints")
with dramatic.output.at_speed(30):
main()
Example context manager usage:
Dramatic Decorator
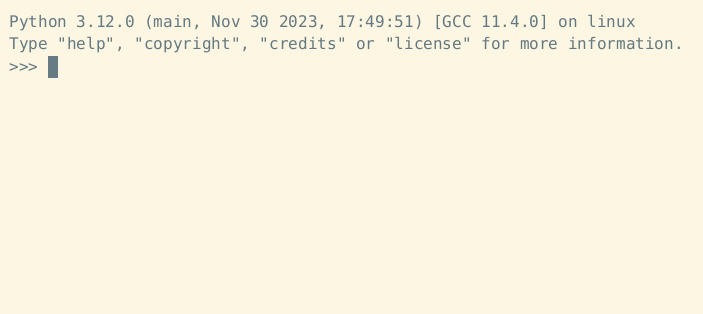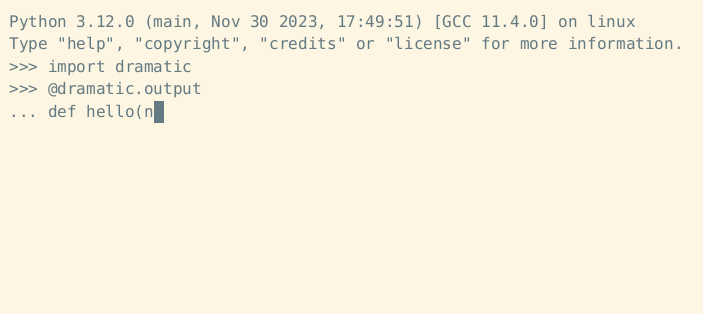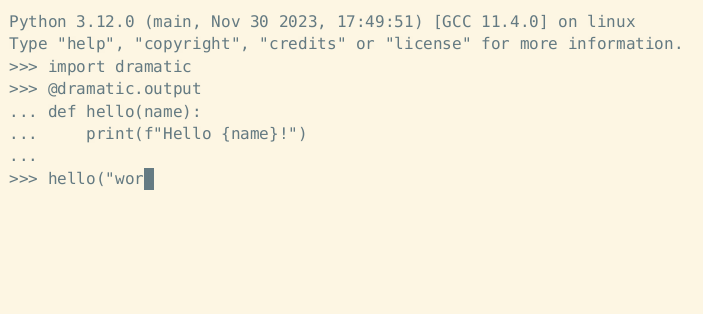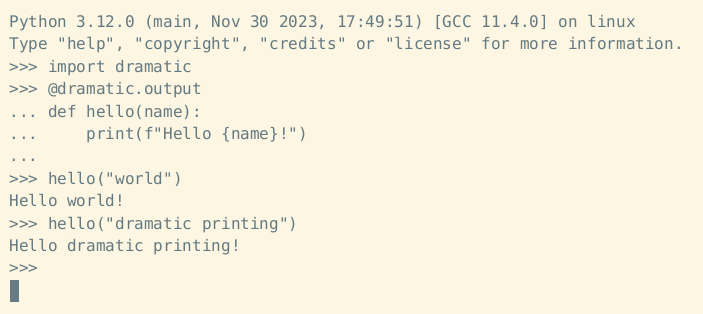
The dramatic.output decorator will cause all standard output and standard error to display dramatically while the decorated function is running:
import dramatic
@dramatic.output
def main():
print("This function prints")
main()
The at_speed method works as a decorator as well:
import dramatic
@dramatic.output.at_speed(30)
def main():
print("This function prints")
main()
Example decorator usage:
Manually Starting and Stopping
Instead of enabling dramatic printing temporarily with a context manager or decorator, the dramatic.start function may be used to enable dramatic printing:
import dramatic
def main():
print("This function prints")
dramatic.start()
main()
The speed keyword argument may be used to change the printing speed (in characters per second):
import dramatic
def main():
print("This function prints")
dramatic.start(speed=30)
main()
To make only standard output dramatic (but not standard error) pass stderr=False to start:
import dramatic
def main():
print("This function prints")
dramatic.start(stderr=False)
main()
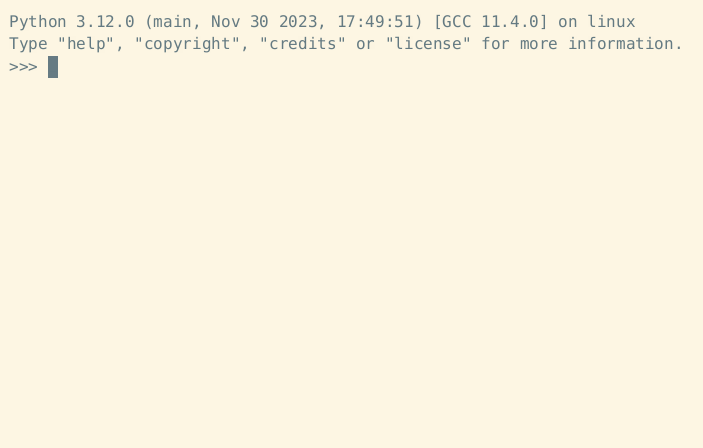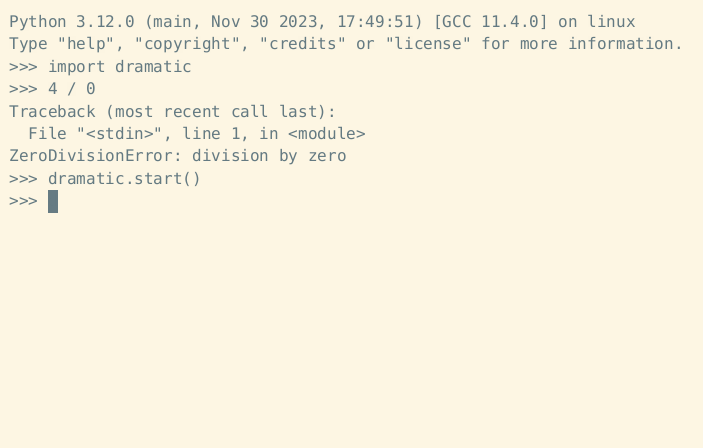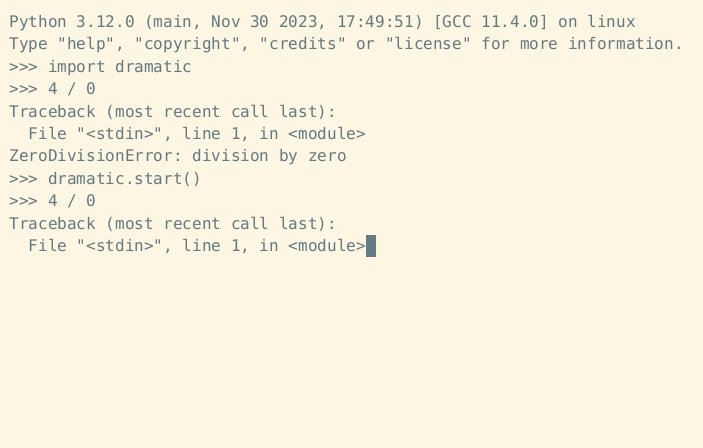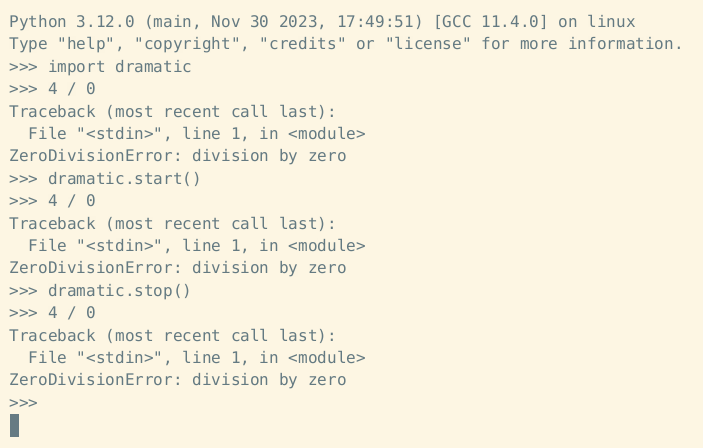
To disable dramatic printing, the dramatic.stop function may be used.
Here's an example context manager that uses both dramatic.start and dramatic.stop:
import dramatic
class CustomContextManager:
def __enter__(self):
print("Printing will become dramatic now")
dramatic.start()
def __exit__(self):
dramatic.stop()
print("Dramatic printing has stopped")
Example start and stop usage:
Dramatic Print
The dramatic.print function acts just like the built-in print function, but it prints dramatically:
import dramatic
dramatic.print("This will print some text dramatically")
Other Features
Pressing Ctrl-C while text is printing dramatically will cause the remaining text to print immediately.
To start a dramatic Python REPL:
$ python3 -m dramatic
>>>
To dramatically run a Python module:
$ python3 -m dramatic -m this
To dramatically run a Python file:
$ python3 -m dramatic hello_world.py
The dramatic module also accepts a --speed argument to set the characters printed per second.
In this example we're increasing the speed from 75 characters-per-second to 120:
Dramatic By Default
Want to make your Python interpreter dramatic by default?
Creating a Python startup file and setting the PYTHONSTARTUP environment variable to its filename will run some code each time the Python interpreter launches.
Add this code to your Python startup file to make your Python REPL dramatic by default:
try:
import dramatic, sys
sys.__interactivehook__ = dramatic.start
del dramatic, sys
except ImportError:
pass
Want to make every Python program dramatic?
You'll need to make a usercustomize.py in your user site packages directory.
Find this directory with:
$ python -c "import site; print(site.getusersitepackages())"
And create a usercustomize.py file in that directory, with this in it:
import dramatic, sys
dramatic.start()
del dramatic, sys
Note that the dramatic module will need to be installed globally for this to work.
To make Python dramatic within virtual environments you'll need to use a sitecustomize.py file in your virtual environments "site packages" directory instead.
Credits
This package was inspired by the dramatic print Python Morsels exercise, which was partially inspired by Brandon Rhodes' adventure Python port (which displays its text at 1200 baud).
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.