Language Model for Question Generation.
Project description
Generative Language Models for Paragraph-Level Question Generation

This is the official repository of the paper "Generative Language Models for Paragraph-Level Question Generation, EMNLP 2022 main conference". This repository includes following contents:
- QG-Bench, the first ever multilingual/multidomain QG benchmark.
- Multilingual/multidomain QG models fine-tuned on QG-Bench.
- A python library
lmqgdeveloped for question generation in python as well as QG model fine-tuning/evaluation. - AutoQG, a web application hosting QG models where user can test the model output interactively.
Table of Contents
- QG-Bench: multilingual & multidomain QG datasets (+ fine-tuned models)
- LMQG: python library to fine-tune/evaluate QG model
- AutoQG: web application hosting multilingual QG models
- RestAPI: run model prediction via restAPI
Please cite following paper if you use any resource:
@inproceedings{ushio-etal-2022-generative,
title = "{G}enerative {L}anguage {M}odels for {P}aragraph-{L}evel {Q}uestion {G}eneration",
author = "Ushio, Asahi and
Alva-Manchego, Fernando and
Camacho-Collados, Jose",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing",
month = dec,
year = "2022",
address = "Abu Dhabi, U.A.E.",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
}
LMQG: Language Model for Question Generation 🚀
The lmqg is a python library to fine-tune seq2seq language models (T5, BART)
on the question generation task and provide an API to host the model prediction via huggingface.
Let's install lmqg via pip first.
pip install lmqg
Generate Question & Answer
- Generate Question on Answers: This is a basic usecase of our QG models, where user provides a paragraph and an answer to generate a question that is answerable by the answer given the paragraph. See MODEL CARD for the available models.
from lmqg import TransformersQG
# initialize model
model = TransformersQG(language='en', model='lmqg/t5-large-squad-qg')
# a list of paragraph
context = [
"William Turner was an English painter who specialised in watercolour landscapes",
"William Turner was an English painter who specialised in watercolour landscapes"
]
# a list of answer (same size as the context)
answer = [
"William Turner",
"English"
]
# model prediction
question = model.generate_q(list_context=context, list_answer=answer)
print(question)
[
'Who was an English painter who specialised in watercolour landscapes?',
'What nationality was William Turner?'
]
- Generate Question & Answer Pairs: Instead of specifying an answer, user can let QG model to generate an answer on the paragraph, and generate question on it sequentially.
This functionality is only available for the QG models fine-tuned with answer extraction see MODEL CARD for the full list of models with answer extraction (model alias usually has a suffix of
-qg-ae).
from lmqg import TransformersQG
# initialize model
model = TransformersQG(language='en', model='lmqg/t5-large-squad-qg-ae')
# paragraph to generate pairs of question and answer
context = "William Turner was an English painter who specialised in watercolour landscapes. He is often known as William Turner of Oxford or just Turner of Oxford to distinguish him from his contemporary, J. M. W. Turner. Many of Turner's paintings depicted the countryside around Oxford. One of his best known pictures is a view of the city of Oxford from Hinksey Hill."
# model prediction
question_answer = model.generate_qa(context)
# the output is a list of tuple (question, answer)
print(question_answer)
[
('Who was an English painter who specialised in watercolour landscapes?', 'William Turner'),
("What was William Turner's nickname?", 'William Turner of Oxford'),
("What did many of Turner's paintings depict around Oxford?", 'countryside'),
("What is one of William Turner's best known paintings?", 'a view of the city of Oxford')
]
Model Evaluation
The evaluation tool reports BLEU4, ROUGE-L, METEOR, BERTScore, and MoverScore following QG-Bench.
From command line, run following command
lmqg-eval -m "lmqg/t5-large-squad-qg" -e "./eval_metrics" -d "lmqg/qg_squad" -l "en"
where -m is a model alias on huggingface or path to local checkpoint, -e is the directly to export the metric file, -d is the dataset to evaluate, and -l is the language of the test set.
Instead of running model prediction, you can provide a prediction file instead to avoid computing it each time.
lmqg-eval --hyp-test '{your prediction file}' -e "./eval_metrics" -d "lmqg/qg_squad" -l "en"
The prediction file should be a text file of model generation in each line in the order of test split in the target dataset
(sample).
Check lmqg-eval -h to display all the options.
Model Training
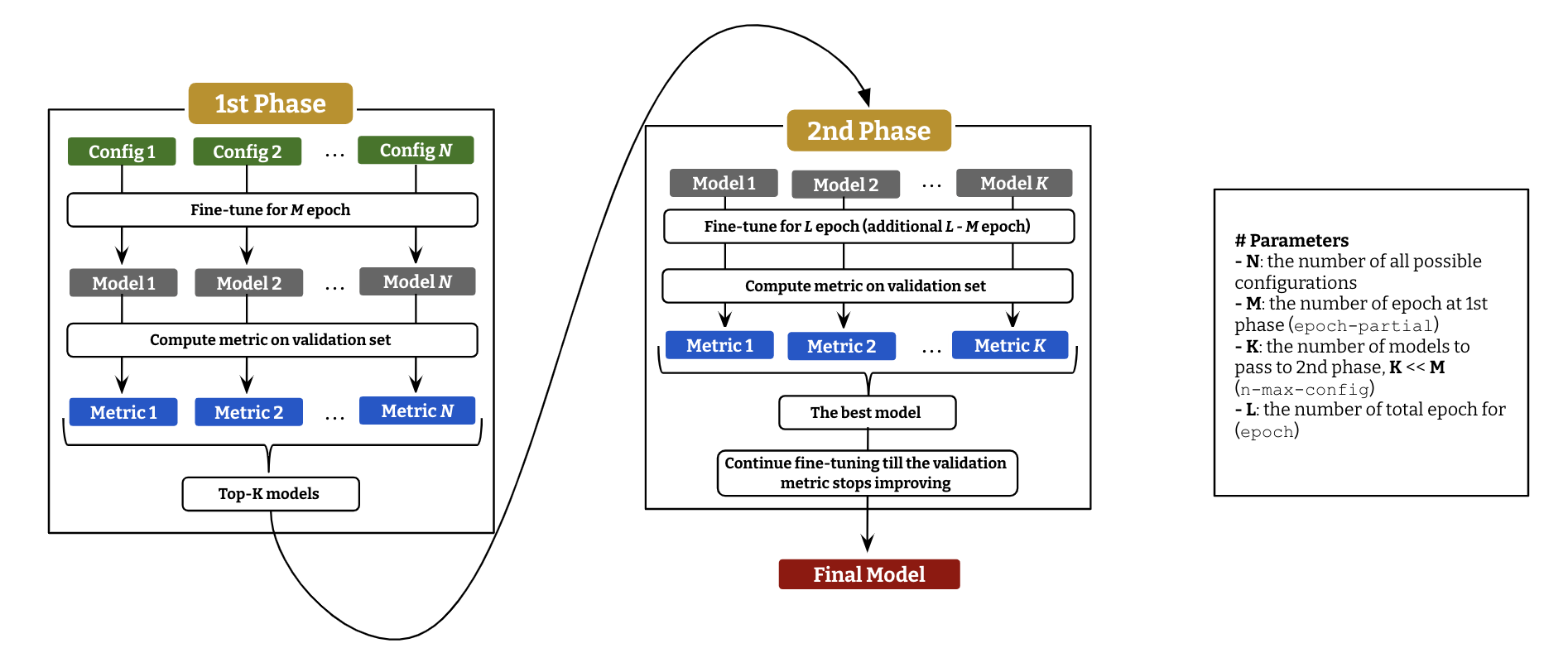
To fine-tune QG model, we employ a two-stage hyper-parameter optimization, described as above diagram. Following command is to run the fine-tuning with parameter optimization.
lmqg-train-search -c "tmp_ckpt" -d "lmqg/qg_squad" -m "t5-small" -b 64 --epoch-partial 5 -e 15 --language "en" --n-max-config 1 \
-g 2 4 --lr 1e-04 5e-04 1e-03 --label-smoothing 0 0.15
Check lmqg-train-search -h to display all the options.
Fine-tuning models in python follows below.
from lmqg import GridSearcher
trainer = GridSearcher(
checkpoint_dir='tmp_ckpt',
dataset_path='lmqg/qg_squad',
model='t5-small',
epoch=15,
epoch_partial=5,
batch=64,
n_max_config=5,
gradient_accumulation_steps=[2, 4],
lr=[1e-04, 5e-04, 1e-03],
label_smoothing=[0, 0.15]
)
trainer.run()
AutoQG
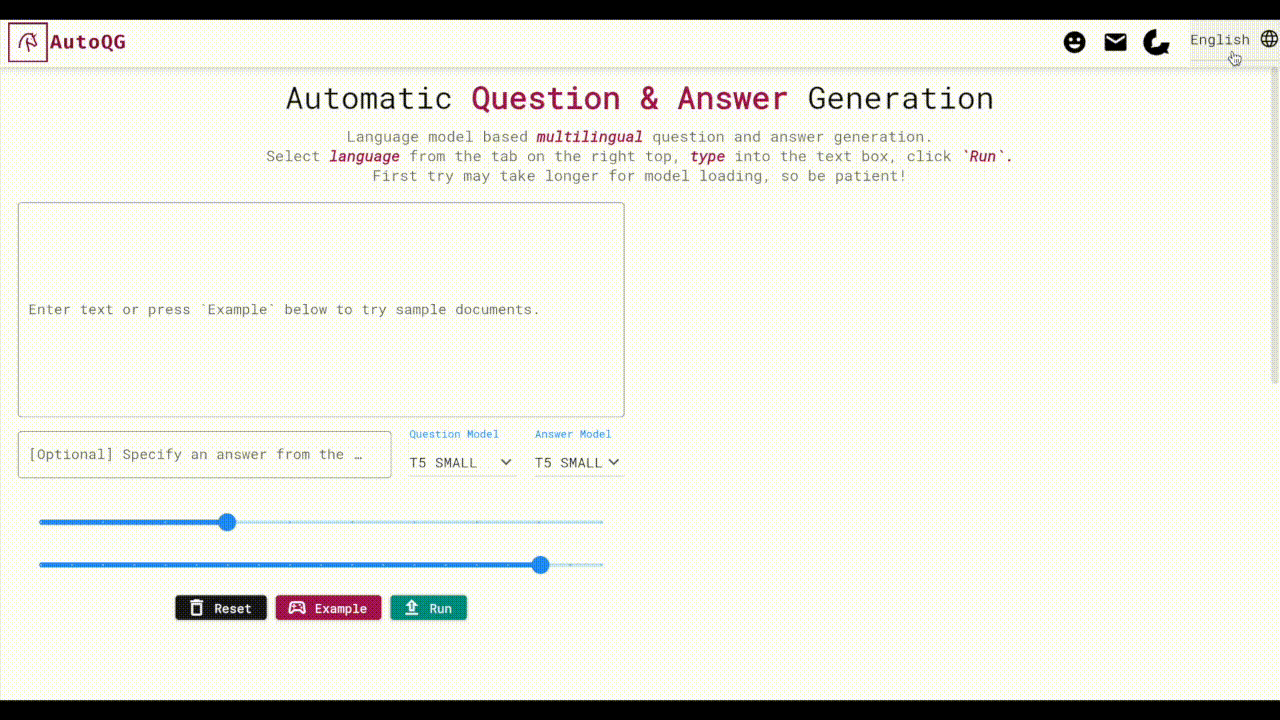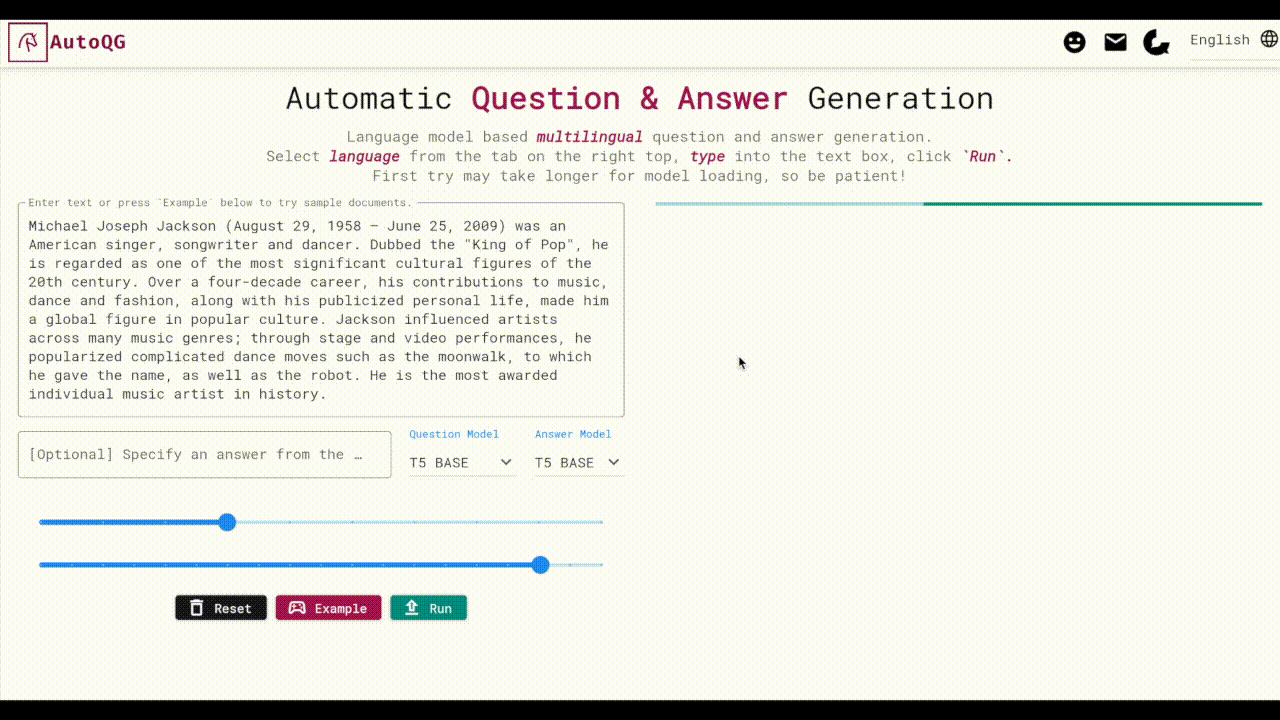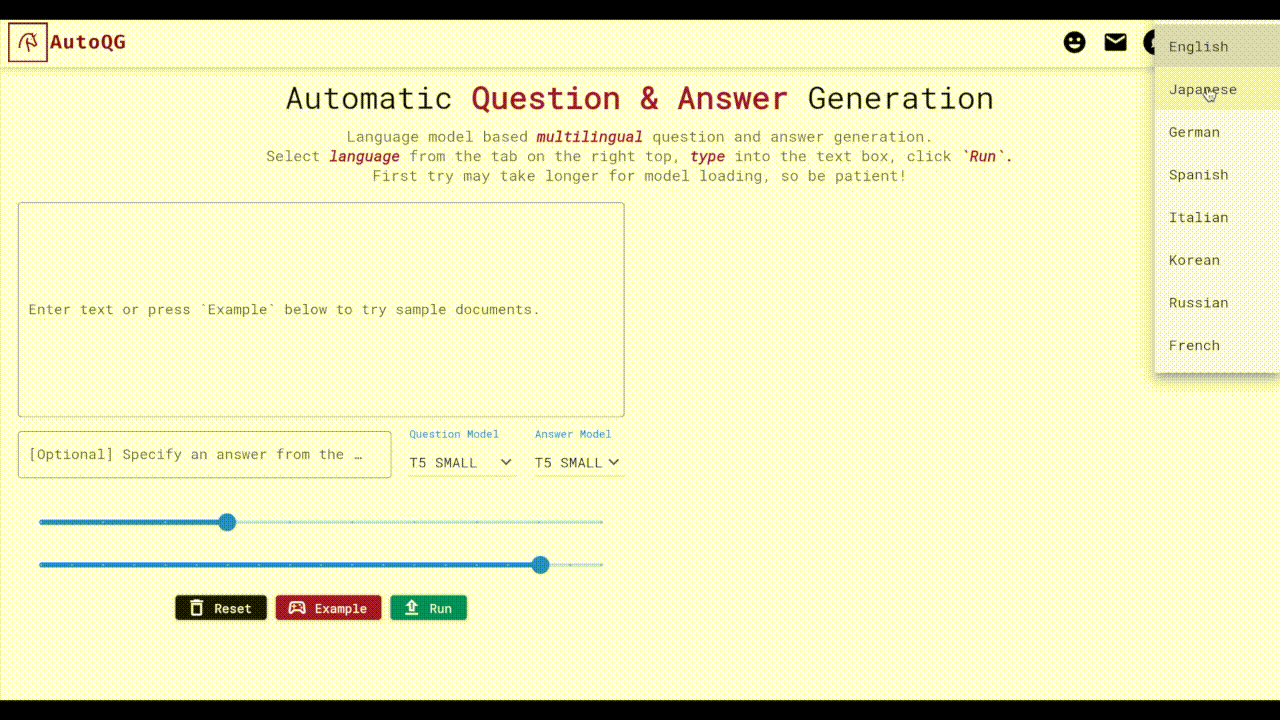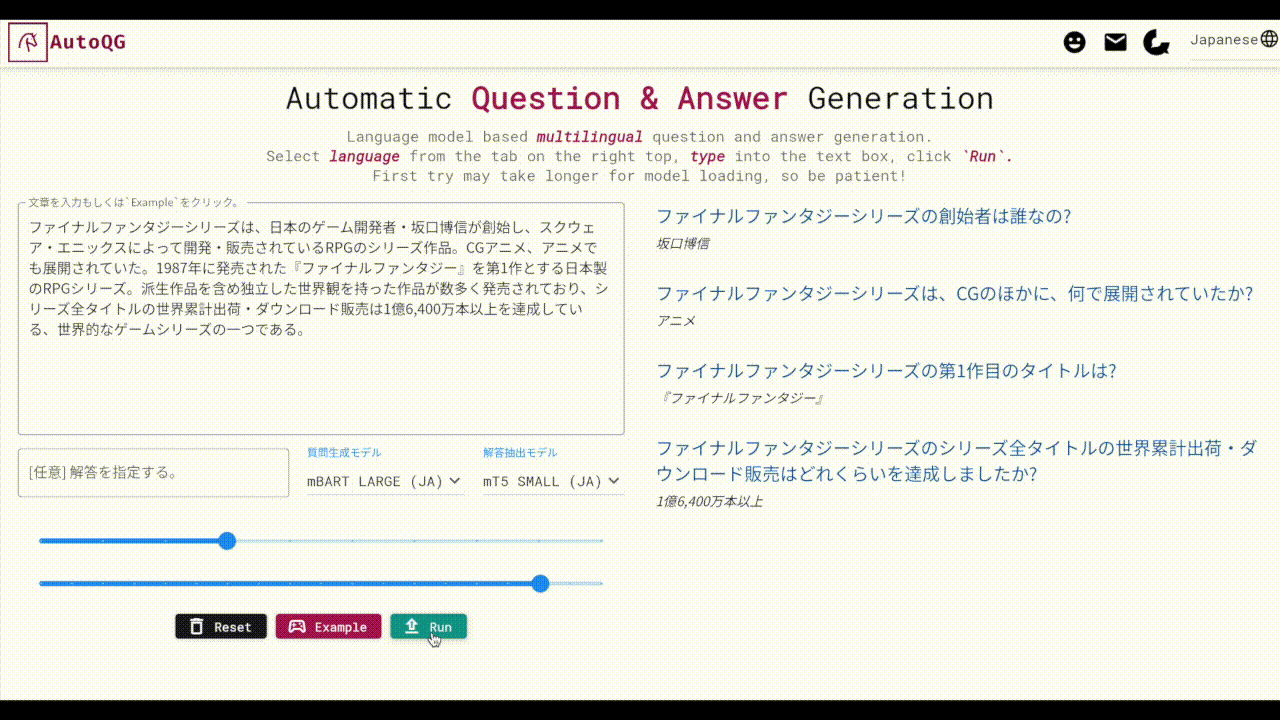
AutoQG (https://autoqg.net) is a free web application hosting our QG models. The QG models are listed at the QG-Bench page.
Rest API with huggingface inference API
We provide a rest API which hosts the model inference through huggingface inference API. You need huggingface API token to run your own API and install dependencies as below.
pip install lmqg[api]
Swagger UI is available at http://127.0.0.1:8088/docs, when you run the app locally (replace the address by your server address).
Build
- Build/Run Local (command line):
export API_TOKEN={Your Huggingface API Token}
uvicorn app:app --reload --port 8088
uvicorn app:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8088
- Build/Run Local (docker):
docker build -t lmqg/app:latest . --build-arg api_token={Your Huggingface API Token}
docker run -p 8080:8080 lmqg/app:latest
API Description
You must pass the huggingface api token via the environmental variable API_TOKEN.
The main endpoint is question_generation, which has following parameters,
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| input_text | input text, a paragraph or a sentence to generate question |
| language | language |
| qg_model | question generation model |
| answer_model | answer extraction model |
and return a list of dictionaries with question and answer.
{
"qa": [
{"question": "Who founded Nintendo Karuta?", "answer": "Fusajiro Yamauchi"},
{"question": "When did Nintendo distribute its first video game console, the Color TV-Game?", "answer": "1977"}
]
}
Misc
Following link is useful if you need to reproduce the results in our paper.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
















