An advanced PID controller
Project description
moat-lib-pid
An advanced PID controller in Python. The derivative term can also be used in practice thanks to built-in first-order filter. Detailed information can be found here.
Usage is very simple:
from moat.lib.pid import PID
# Create PID controller
pid = PID(Kp=2.0, Ki=0.1, Kd=1.0, Tf=0.05)
# Control loop
while True:
# Get current measurement from system
timestamp, measurement = system.get_measurement()
# Calculate control signal by using PID controller
reference = 1.0
control = pid(timestamp, reference - measurement)
# Feed control signal to system
system.set_input(control)
This module was vendorized from the advanced-pid module by Erkan Adali erkanadali91@gmail.com.
Complete API documentation can be found here.
Usage
Biggest advantage of advanced-pid, the derivative term has a built-in first-order
filter.
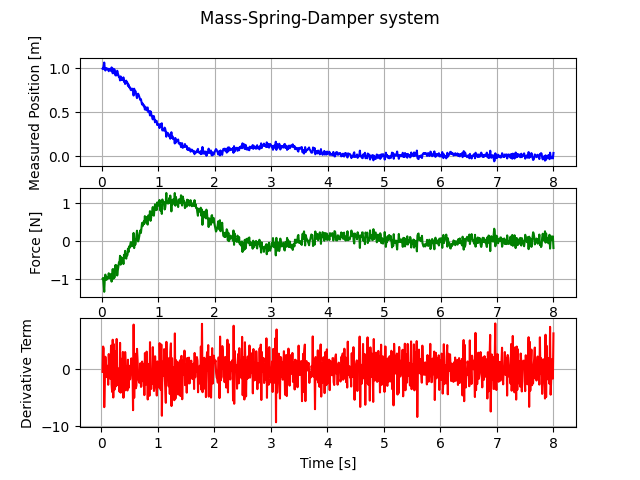
advanced-pid package includes a toy mass-spring-damper system model for testing:
from moat.lib.pid import PID
from examples.mass_spring_damper import MassSpringDamper
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from numpy import diff
# Create a mass-spring-damper system model
system = MassSpringDamper(mass=1.0, spring_const=1.0, damping_const=0.2)
system.set_initial_value(initial_position=1.0, initial_velocity=0.0)
# Create PID controller
pid = PID(Kp=1.0, Ki=0.0, Kd=2.0, Tf=0.5)
# Control loop
time, meas, cont = [], [], []
for i in range(800):
# Get current measurement from system
timestamp, measurement = system.get_measurement()
# Calculate control signal by using PID controller
control = pid(timestamp, -measurement)
# Feed control signal to system
system.set_input(control)
# Record for plotting
time.append(timestamp)
meas.append(measurement)
cont.append(control)
# Plot result
fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(3, 1)
fig.suptitle('Mass-Spring-Damper system')
ax1.set_ylabel('Measured Position [m]')
ax1.plot(time, meas, 'b')
ax1.grid()
ax2.set_ylabel('Force [N]')
ax2.plot(time, cont, 'g')
ax2.grid()
ax3.set_xlabel('Time [s]')
ax3.set_ylabel('Derivative Term')
ax3.plot(time[1:], diff(meas)/diff(time), 'r')
ax3.grid()
plt.show()
As It can be seen in the figure, derivative term cannot be use without a filter:
Installation
To install, run:
pip3 install moat-lib-pid
Tests
To run tests, run:
pytest tests
License
Licensed under the MIT License.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Hashes for moat_lib_pid-0.6.1-py3-none-any.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 3723541e53f8d607d932bf3b46e2338d0c4e7d9c2f7ceb4d7c3e8924fc8f5b05 |
|
| MD5 | 361e0ad68feb00e8e3a71bb502548821 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | bccea1f67c392ed1d38a652e7db5f06a4b4e387752cc51bfcb1ff46bfacf900b |