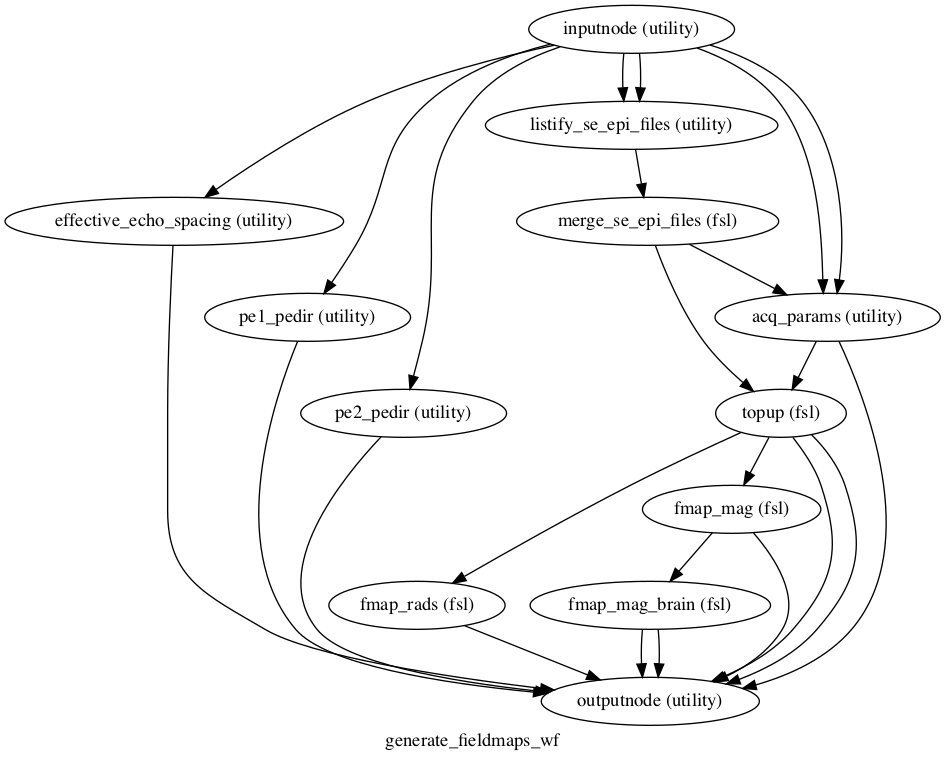
Nipype workflow to generate fieldmaps from EPI acquisitions with differing phase-encoding directions
Project description
nipype-generate-fieldmaps
Nipype workflow to generate fieldmaps from EPI acquisitions with differing phase-encoding directions
Installation
pip install nipype-generate-fieldmaps
Usage
As a stand-alone workflow
# create the workflow
wf = create_generate_fieldmaps_wf()
# wire-up the inputs
wf.inputs.inputnode.se_epi_pe1_file = my_se_epi_pe1_file # type: str | Path
wf.inputs.inputnode.se_epi_pe2_file = my_se_epi_pe2_file # type: str | Path
wf.inputs.inputnode.se_epi_pe1_sidecar_file = my_se_epi_pe1_sidecar_file # type: str | Path
wf.inputs.inputnode.se_epi_pe2_sidecar_file = my_se_epi_pe2_sidecar_file # type: str | Path
# set the output directory
wf.base_dir = my_output_dir # type: str | Path
# run it
wf.run()
As a nested workflow
The nodes node1, node2, some_other_node, maybe_a_4th_node, epi_node, and anat_node are made up for demonstration purposes
from nipype import Workflow
from nipype.interfaces.fsl import EpiReg
from nipype_generate_fieldmaps import create_generate_fieldmaps_wf
# parent workflow defined elsewhere
wf = Workflow(...)
# create the (sub-)workflow
fmap_wf = create_generate_fieldmaps_wf()
# connect the various nodes form the parent workflow to the nested fieldmap workflow
wf.connect(node1, 'out_file', fmap_wf, 'inputnode.se_epi_pe1_file')
wf.connect(node2, 'out', fmap_wf, 'inputnode.se_epi_pe2_file')
wf.connect(some_other_node, 'output_file', fmap_wf, 'inputnode.se_epi_pe1_sidecar_file')
wf.connect(maybe_a_4th_node, 'sidecar_file', fmap_wf, 'inputnode.se_epi_pe2_sidecar_file')
# connect the fieldmap workflow outputs to one (or more) node(s) in the parent workflow
# for example: EpiReg()
epireg = Node(EpiReg(out_base='epi2str.nii.gz'), name='epi_reg')
# from elsewhere
wf.connect(epi_node, 'my_epi_file' epireg, 'epi')
wf.connect(anat_node, 'my_t1_file', epireg, 't1_head')
wf.connect(anat_node, 'my_t1_brain_file', epireg, 't1_brain')
# from the fieldmap workflow!
wf.connect(fmap_wf, 'outputnode.fmap_rads_file', epireg, 'fmap')
wf.connect(fmap_wf, 'outputnode.fmap_mag_file', epireg, 'fmapmag')
wf.connect(fmap_wf, 'outputnode.fmap_mag_brain_file', epireg, 'fmapmagbrain')
wf.connect(fmap_wf, 'outputnode.echo_spacing', epireg, 'echospacing')
wf.connect(fmap_wf, 'outputnode.pe1_pedir', epireg, 'pedir')
From the command line
$ nipype-generate-fieldmaps --help
usage: nipype-generate-fieldmaps [-h] [-v] se_epi_pe1 se_epi_pe2 se_epi_pe1_sidecar se_epi_pe2_sidecar out_dir
Generate fieldmaps from EPI acquisitions with differing phase-encoding directions
positional arguments:
se_epi_pe1 The spin-echo EPI file acquired in the 'first' phase-encoding direction
se_epi_pe2 The spin-echo EPI file acquired in the 'second' phase-encoding direction
se_epi_pe1_sidecar The JSON sidecar for the first spin-echo EPI file
se_epi_pe2_sidecar The JSON sidecar for the second spin-echo EPI file
out_dir The directory into which outputs are written
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v, --version show program's version number and exit
Prerequisites
This workflow has a few requirements:
-
There are two acquisitions (i.e.
.nii.gzfiles) acquired with different phase encodings, usually opposite phase encodings but this need not be the case. -
The number of volumes in acquisition 1 (the first phase encoding direction) equals the number of volumes in acquisition 2 (the second phase encoding direction)
-
Each acquisition has a JSON sidecar. Specifically, this workflow requires that each sidecar contain one of the following sets of properties. These properties are listed in the order in which the workflow will search:
PhaseEncodingDirectionandTotalReadoutTime, orPhaseEncodingDirection,ReconMatrixPE, andEffectiveEchoSpacing, orPhaseEncodingDirection,ReconMatrixPE, andBandwidthPerPixelPhaseEncode
If either JSON sidecar fails to contain at least one of the above sets of parameters the workflow will produce an error.
I/O
This workflow requires 4 inputs to be connected to the node named inputnode:
-
se_epi_pe1_fileThe spin-echo EPI file acquired in the 'first' phase-encoding direction
-
se_epi_pe2_fileThe spin-echo EPI file acquired in the 'second' phase-encoding direction
-
se_epi_pe1_sidecar_fileThe JSON sidecar for the first spin-echo EPI file
-
se_epi_pe2_sidecar_fileThe JSON sidecar for the second spin-echo EPI file
This workflow also exposes the following outputs via the node named outputnode:
-
acq_params_fileThe computed file passed to the
--datainoption oftopup -
corrected_se_epi_fileThe
.nii.gzimage containing all distortion corrected volumes from the two input acquisitions -
fmap_hz_fileThe fieldmap in hertz (Hz)
-
fmap_rads_fileThe fieldmap in radians per second (rad/s)
-
fmap_mag_fileThe 'magnitude' image (mean image) computed by averaging all volumes in
corrected_se_epi_file -
fmap_mag_brain_fileThe result of applying brain-extraction to
fmap_mag_file -
fmap_mag_brain_mask_fileThe brain mask produced during the brain-extraction of
fmap_mag_file
Workflow diagram
Contributing
- Have or install a recent version of
poetry(version >= 1.1) - Fork the repo
- Setup a virtual environment (however you prefer)
- Run
poetry install - Run
pre-commit install - Add your changes
- Commit your changes + push to your fork
- Open a PR
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Hashes for nipype-generate-fieldmaps-0.2.4.tar.gz
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | ff1d47eaca3bb2bfa0add569349ec94aca840b218513ee267168f1755a5cca95 |
|
| MD5 | b095addc803f86668d03a7ac89d91c74 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 0e8befd8c85bf8432a2e921235f615cb3defa0ed3f8616ef4938a66e5a1201f4 |
Hashes for nipype_generate_fieldmaps-0.2.4-py3-none-any.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 1d00c11362a158cf1728a798092b8af26a6864951a40abb7d51fa499166aad1a |
|
| MD5 | 6bd19f00338c7984367b2cbbe1f329ae |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | d17b9d314ed38138f9a45464ba80c71eeb485558e18dcd606e50646abb66e3c3 |