No project description provided
Project description
OptiLog: A Framework for SAT-based Systems
OptiLog is a new Python framework for rapid prototyping of SAT-based systems. OptiLog includes functionality for loading and creating formulas, state of the art SAT solvers, high level formula modelling, pseudo boolean and cardinality encodings, automatic configuration and experiment running and parsing.
OptiLog is designed to be simple and efficient. OptiLog can be used by field experts for tasks such as algorithm design, research and benchmarking, but it has also been successfully deployed in undergraduate Computation Logic courses. Moreover, OptiLog has been designed from the ground up to be modular and extensible through the abstract iSAT C++ interface.
Why OptiLog
OptiLog has a fully modular dynamic Python binding generator for SAT solvers. This means that integrating new SAT solvers into OptiLog is as simple as implementing a C++ interface, and doesn't require any Python C API knowledge!
On top of that, OptiLog provides all the functionality required to develop and deploy complete SAT-based systems. We provide access to state of the art automatic configuration tools to configure any kind of algorithm (not limited to SAT). And run experiments and parse logs.
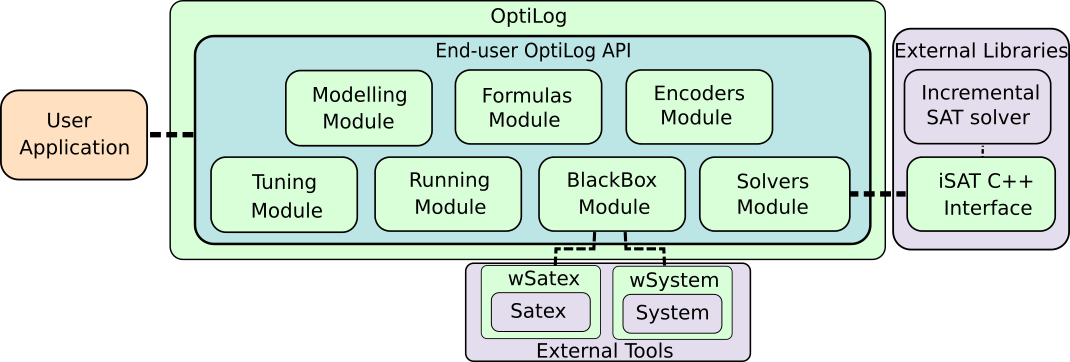
Architecture
The main architecture of OptiLog is composed of the five main modules of the end-user OptiLog API that supports the creation of SAT based systems and the iSAT interface for SAT solver developers.
-
The Formula module: The Formula module provides classes for the manipulation of SAT, MaxSAT and QBF formulas.
-
The SAT Solver module: The SAT Solver module provides bindings through the Python Interface PyiSAT to SAT solvers implementing the iSAT interface.
-
The PB Encoder module: The PB Encoder module provides access to encoders Pseudo-Boolean and Cardinality into SAT.
-
The Automatic Configuration module: The Automatic Configuration module provides support to automatically configure Python functions.
-
The Solver Runner module: The Solver Runner module provides support to automatically generate execution scenarios that run experiments and collect logs.
SAT solver Examples
OptiLog deals with boolean variables represented by positive integers (DIMACS).
Here is an example using the well known Glucose41:
>>> from optilog.sat import Glucose41
>>> solver = Glucose41()
>>> solver.add_clause([1, 3])
>>> solver.add_clause([-1, -2])
>>> solver.solve(assumptions=[1])
True
>>> solver.model()
[1, -2, -3]
All SAT solvers are incremental, which means new clauses can be added after a solver has found a model:
>>> from optilog.sat import Glucose41
>>> solver = Glucose41()
>>> solver.add_clause([1, -2])
>>> solver.solve(assumptions=[1, 2])
True
>>> solver.model()
[1, 2]
>>> solver.add_clause([-1, -2])
>>> solver.solve(assumptions=[1, 2])
False
>>> solver.core()
[1]
CNF and WCNF formulas can also be directly loaded in to the solver:
>>> from optilog.sat import Glucose41
>>> solver = Glucose41()
>>> solver.load_cnf('./path/to/file')
Integrating a SAT solver
Adding a new SAT solver to OptiLog is super easy. Just create a class that implements your desired method of the iSAT interface. Here you can see an example of the Cadical wrapper implementing the addClause and solve methods:
CadicalWrapper::CadicalWrapper()
{
solver = new CaDiCaL::Solver;
}
CadicalWrapper::~CadicalWrapper()
{
delete solver;
}
void CadicalWrapper::addClause(const std::vector<int>& literals)
{
for (auto i = literals.begin(); i != literals.end(); ++i)
{
solver->add(*i);
}
solver->add(0);
}
E_STATE CadicalWrapper::solve(const std::vector<int>& assumptions)
{
for (auto i = assumptions.begin(); i != assumptions.end(); ++i)
{
solver->assume(*i);
}
return (solver->solve() == 10 ? E_STATE::SAT : E_STATE::UNSAT);
}
OPTILOG_C_INTERFACE(CadicalWrapper, "Cadical")
Then, the solver is compiled as a shared library and integrated into OptiLog by copying the library on the ~/.optilog_solvers/ directory. Please checkout the documentation for more details on how to integrate a SAT solver and add configurable parameters.
Installation
OptiLog requires Python 3.6+ and a Linux installation. Current wheels are distributed on PyPi for the latest release.
Simply run:
$ pip install optilog
Documentation is available online
License & Documentation
OptiLog is free to use for academic use cases. For industrial use please contact the authors.
For more information you can find the full license here: License
Cite
@InProceedings{10.1007/978-3-030-80223-3_1,
author="Ans{\'o}tegui, Carlos
and Ojeda, Jes{\'u}s
and Pacheco, Antonio
and Pon, Josep
and Salvia, Josep M.
and Torres, Eduard",
editor="Li, Chu-Min
and Many{\`a}, Felip",
title="OptiLog: A Framework for SAT-based Systems",
booktitle="Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing -- SAT 2021",
year="2021",
publisher="Springer International Publishing",
address="Cham",
pages="1--10",
abstract="We present OptiLog, a new Python framework for rapid prototyping of SAT-based systems. OptiLog allows to use and integrate SAT solvers currently developed in C/C++ just by implementing the iSAT C++ interface. It also provides a Python binding to the PBLib C++ toolkit for encoding Pseudo Boolean and Cardinality constraints. Finally, it leverages thepower of automatic configurators by allowing to easily create configuration scenarios including multiple solvers and encoders.",
isbn="978-3-030-80223-3"
}
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distributions
Built Distributions
Hashes for optilog-0.2.0-cp39-cp39-manylinux_2_17_x86_64.manylinux2014_x86_64.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 30a02ba6dceba40170820af9ad9a591e2bc8b910f8d964b80c67f2f6a27ab2fe |
|
| MD5 | b39af16ba675532c8f63a0886fe7297e |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | c67edbe7a7b3f54a8c13b266e78e49020e4a1027fa72e58a46b46afb4e92389f |
Hashes for optilog-0.2.0-cp38-cp38-manylinux_2_17_x86_64.manylinux2014_x86_64.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 23e6b7ab4bf57882f084c4f9d2f9c38a1f86424b232449cbd317d41d1fae65e5 |
|
| MD5 | 9a09ff99f2252324bfb88361df0d3985 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 4875ac26366b06adfb247f09e15cee6c12d8bcd6258da311b48f265cd1362c36 |
Hashes for optilog-0.2.0-cp37-cp37m-manylinux_2_17_x86_64.manylinux2014_x86_64.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | a9f0bc4e0e62e22c9978453aaf463a8ac2f7eb808e8e38f310f59742f4836ab4 |
|
| MD5 | 0fe51cc11cb0a3f272f73d0a64e44ecc |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 6ef07b24873e50e07574348bbb8fee6b9c2f80e55d3a19a2c29a598f137fc650 |
Hashes for optilog-0.2.0-cp36-cp36m-manylinux_2_17_x86_64.manylinux2014_x86_64.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 3c1ceac5c3925915f44ef257e860cc7336e9bcb3972a76a0584872f86dcbef22 |
|
| MD5 | 75da0593b8275ce3d54216878f421758 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | cb6c1afa2fc15eb08dcb11afa797f6340fb2c05a26924e43ac6dcd6ce5fb830f |