Linear Feedback Shift Register
Project description
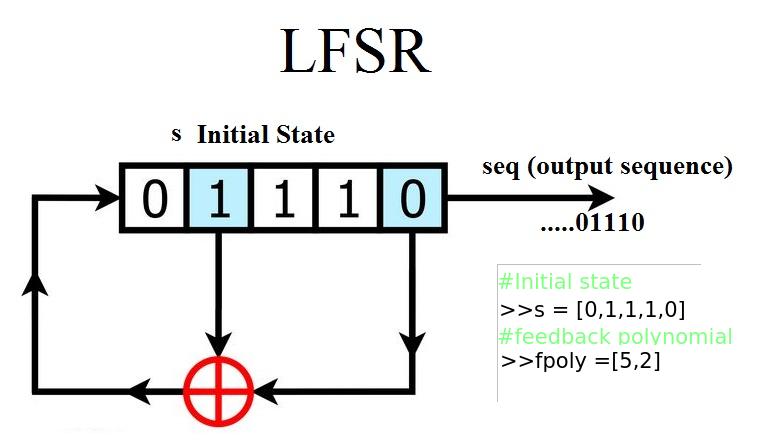
LFSR -Linear Feedback Shift Register
View on Github Page
Python
Requirement : numpy
Example ## 5 bit LFSR with x^5 + x^2 + 1
>>>import numpy as np
>>>from lfsr import LFSR
>>>L = LFSR()
>>>L.info()
5 bit LFSR with feedback polynomial x^5 + x^2 + 1
Expected Period (if polynomial is primitive) = 31
Current :
State : [1 1 1 1 1]
Count : 0
Output bit : -1
feedback bit : -1
>>>L.next()
>>>L.runKCycle(10)
>>>L.runFullCycle()
>>>L.info()
Example ## 5 bit LFSR with custum state and feedback polynomial
>>>state = [0,0,0,1,0]
>>>fpoly = [5,4,3,2]
>>>L = LFSR(fpoly=fpoly,initstate =state, verbose=True)
>>>L.info()
>>>tempseq = L.runKCycle(10)
>>>L.set(fpoly=[5,3])
Example 3 ## 23 bit LFSR with custum state and feedback polynomial
>>>L = LFSR(fpoly=[23,18],initstate ='random',verbose=True)
>>>L.info()
>>>L.runKCycle(10)
>>>L.info()
>>>seq = L.seq
Changing feedback polynomial in between as in Enhancement of A5/1
>>>L.changeFpoly(newfpoly =[23,14],reset=False)
>>>seq1 = L.runKCycle(20)
>>>L.changeFpoly(newfpoly =[23,9],reset=False)
>>>seq1 = L.runKCycle(20)
For A5/1 GSM Stream cipher generator (Hint)
# Three LFSRs initialzed with 'ones' though they are intialized with encription key
R1 = LFSR(fpoly = [19,18,17,14])
R2 = LFSR(fpoly = [23,22,21,8])
R3 = LFSR(fpoly = [22,21])
# clocking bits
b1 = R1.state[8]
b2 = R1.state[10]
b3 = R1.state[10]
MATLAB
Genrate randon binary sequence using LFSR for any given feedback taps (polynomial), This will also check Three fundamental Property of LFSR
- (1) Balance Property
- (2) Runlength Property
- (3) Autocorrelation Property
This MATLAB Code work for any length of LFSR with given taps (feedback polynomial) -Universal, There are three files LFSRv1.m an LFSRv2.m, LFSRv3.m
LFSRv1
This function will return all the states of LFSR and will check Three fundamental Property of LFSR (1) Balance Property (2) Runlength Property (3) Autocorrelation Property
EXAMPLE
>>s=[1 1 0 0 1]
>>t=[5 2]
>>[seq c] =LFSRv1(s,t)
LFSRv2
This function will return only generated sequence will all the states of LFSR, no verification of properties are done here. Use this function to avoid verification each time you execute the program.
EXAMPLE
>>s=[1 1 0 0 1]
>>t=[5 2]
>>[seq c] =LFSRv2(s,t)
LFSRv3 (faster)
seq = LFSRv3(s,t,N)
this function generates N bit sequence only. This is faster then other two functions, as this does not gives each state of LFSREXAMPLE
>>s=[1 1 0 0 1]
>>t=[5 2]
>>seq =LFSRv3(s,t,50)
Tips
- If you want to use this function in middle of any program, use LFSRv2 or LFSRv1 with verification =0.
- If you want to make it fast for long length of LFSR,use LFSRv3.m
If any doubt, confusion or feedback please contact me
Nikesh Bajaj
http://nikeshbajaj.in
n[dot]bajaj[AT]qmul[dot]ac[dot]uk
bajaj[dot]nikkey[AT]gmail[dot]com
### PhD Student, Queen Mary University of London & University of GenoaProject details
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.











