Lock context manager implemented via redis SETNX/BLPOP.
Project description




Lock context manager implemented via redis SETNX/BLPOP.
Interface targeted to be exactly like threading.Lock.
Usage
Because we don’t want to require users to share the lock instance across processes you will have to give them names. Eg:
conn = StrictRedis()
with redis_lock.Lock(conn, "name-of-the-lock"):
print("Got the lock. Doing some work ...")
time.sleep(5)
Eg:
lock = redis_lock.Lock(conn, "name-of-the-lock")
if lock.acquire(blocking=False):
print("Got the lock.")
else:
print("Someone else has the lock.")
Avoid dogpile effect in django
The dogpile is also known as the thundering herd effect or cache stampede. Here’s a pattern to avoid the problem without serving stale data. The work will be performed a single time and every client will wait for the fresh data.
To use this you will need django-redis, however, python-redis-lock provides you a cache backend that has a cache method for your convenience. Just install python-redis-lock like this:
pip install "python-redis-lock[django]"
Now put something like this in your settings:
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'redis_lock.django_cache.RedisCache',
'LOCATION': '127.0.0.1:6379',
'OPTIONS': {
'DB': 1
}
}
}
This backend just adds a convenient .lock(name, expire=None) function to django-redis’s cache backend.
You would write your functions like this:
from django.core.cache import cache
def function():
val = cache.get(key)
if val:
return val
else:
with cache.lock(key):
val = cache.get(key)
if val:
return val
else:
# DO EXPENSIVE WORK
val = ...
cache.set(key, value)
return val
Features
based on the standard SETNX recipe
optional expiry
no spinloops at acquire
Implementation
redis_lock will use 2 keys for each lock named <name>:
lock:<name> - a string value for the actual lock
lock-signal:<name> - a list value for signaling the waiters when the lock is released
This is how it works:
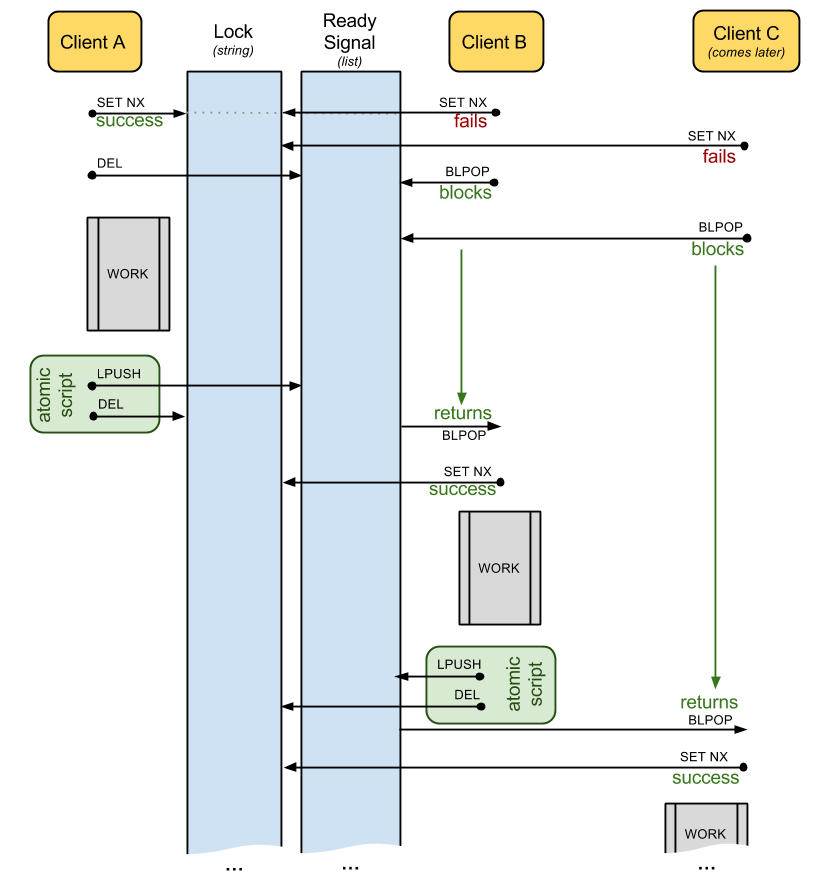
TODO
???
Requirements
Redis 2.6.12 or later.
Python 2.6, 2.7, 3.2, 3.3 and PyPy are supported.
Similar projects
bbangert/retools - acquire does spinloop
distributing-locking-python-and-redis - acquire does polling
cezarsa/redis_lock - acquire does not block
andymccurdy/redis-py - acquire does spinloop
mpessas/python-redis-lock - blocks fine but no expiration

Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.











